- ADJUTANT GENERAL OFFICER (42B) Video
- An adjutant general officer is responsible for providing personnel support that affects Soldiers’ overall welfare and well-being, while assisting commanders by accounting for and keeping Soldiers combat-ready.

- AIR DEFENSE ARTILLERY OFFICER (14A) Video
- The air defense artillery officer leads the air defense artillery branch, who protects U.S. forces from aerial attack, missile attack and enemy surveillance. They must be an expert in tactics, techniques and procedures for the employment of air defense systems.
- They also become an expert in one or more of the following systems: the PATRIOT missile system and the AVENGER system.

- ARMOR OFFICER (19) Video
- Armor officers are responsible for tank and cavalry/forward reconnaissance operations on the battlefield. The role of an armor officer is to be a leader in operations specific to the armor branch and to lead others in many areas of combat operations.

- AVIATION OFFICER (15) Video
- Aviation officers coordinate/lead operations using Army helicopters: OH-58 Kiowa, UH-60 Black Hawk, CH-47 Chinook and the AH-64 Apache. These operations can haul troops and carry supplies, as well as provide quick-strike and long-range target engagement.

- CHAPLAIN (56A) Video
- As an Army chaplain you will have the responsibility of caring for the spiritual well-being of Soldiers and their Families. An Army chaplain’s flock can consist of over 1,500 people.
- The Army chaplaincy is a religiously diverse population reflecting the diversity of the Army, yet each chaplain ministers according to the tenets of his or her distinctive faith community. Unlike most officers in the Army, a chaplain begins serving as a staff officer immediately.

- CHEMICAL OFFICER (74A) Video
- A Chemical, Biological, Radiological and Nuclear officer commands the Army branch that specifically defends against the threat of CBRN weapons and Weapons of Mass Destruction. These officers lead an extraordinary chemical unit that is completely dedicated to protecting our nation.

- ENGINEER OFFICER (12A) Video
- An engineer officer is responsible for providing full support to the wide range of engineering duties in the Army. They can help build structures, develop civil works programs and even provide combat support.

- FIELD ARTILLERY OFFICER (13A) Video
- The field artillery officer leads the field artillery branch, who neutralizes the enemy by cannon, rocket and missile fire. The officer must be an expert in tactics, techniques and procedures for the employment of fire support systems.

- INFANTRY OFFICER (11A) Video
- The infantry officer is responsible for leading the infantry and combined armed forces during land combat.

- MILITARY INTELLIGENCE OFFICER (35) Video
- The Army’s military intelligence is responsible for all collected intelligence during Army missions. They provide essential information that often save the Soldiers fighting on front lines.
- Military Intelligence Officers specialize in these specific areas:
- Imagery Intelligence: Collection and analysis of imagery using photogrammetry and terrain analysis.
- All-Source Intelligence: Performs collection management/surveillance/reconnaissance and provides advice.
- Counterintelligence: Provides coordination and participation in counterintelligence investigations, operations and production.
- Human intelligence: Controlled collection operations and interviews.
- Signals intelligence/electronic warfare: Collects signal intelligence and engages in electronic warfare.
- All-source intelligence aviator: Performs duties as an aviator/MI officer and participates in special electronic mission aircraft missions.

- MILITARY POLICE OFFICER (31A) Video
- A military police officer is responsible for leading the Soldiers that protect lives and property on Army Installations.
- Officers supervise the execution of the five military police Battlefield functions: Maneuver and mobility support operations (reconnaissance and surveillance), Area security operations (site security and response), Law & order operations (law enforcement and developing host-nation police forces), Internment/resettlement operations (military prisoners and enemy combatants), and Police intelligence operations.

- MEDICAL SERVICE CORPS OFFICER (67) Video
- Medical service corps officers command the medical service corps that treats and helps the Soldiers and their families in a variety of areas:
- Behavioral sciences – social workers, clinical psychologists and counseling psychologists
- Health administration services
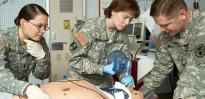
- NURSE CORPS OFFICER (66) Video
- Nurse Corps officers lead a nursing team that cares for Soldiers and their families. As part of the Army Nurse Corps, they play an important role in improving the overall quality of life for Soldiers and their families.

- ORDNANCE OFFICER (91A) Video
- Ordnance officers are responsible for ensuring that weapons systems, vehicles and equipment are ready and available — and in perfect working order — at all times. They also manage the developing, testing, fielding, handling, storage and disposal of munitions.

- QUARTERMASTER OFFICER (92A) Video
- Quartermaster officers are responsible for making sure equipment, materials and systems are available and functioning for missions. More specifically, the quartermaster officer provides supply support for Soldiers and units in field services, aerial delivery, and material and distribution management.

- SIGNAL OFFICER (25A) Video
- The signal officer leads the Signal Corps, which is responsible for the Army’s entire systems of communication. Officers plan and execute all aspects of communication on a mission and are critical to the Army’s continued success.

- TRANSPORTATION OFFICER (88A) Video
- The Transportation Corps is responsible for moving supplies, troops and equipment anywhere on the globe. During war, the Transportation Corps utilizes trucks, boats and airplanes to provide extremely fast support to the combat teams on the frontlines.
- Transportation officers are experts in the systems, vehicles and procedures of moving troops and supplies in the Army.
Careers available with career progression

- CIVIL AFFAIRS OFFICER (38A)
- Civil affairs officers act as a liaison between the Army and civilian authorities and populations.
- The civil affairs officer combines regional expertise, language competency, political-military awareness, cross-cultural communication and professional military skills to conduct civil affairs operations and support civil-military operations in support of conventional and special operations forces.
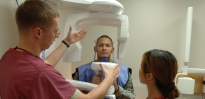
- DENTAL CORPS OFFICER (63)
- An Army Dental Corps officer is responsible for the dental health of Soldiers and their families. They are also responsible for providing health care to Soldiers’ families and others eligible to receive this care in the military community.
- During combat, the Dental Corps officer assists in the emergency medical management of casualties.
- Within the Army Dental Corps, you can specialize in the following areas: Comprehensive Dentistry, Endodontics, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Orthodontics, Pediatric Dentistry, and Periodontics.

- ARMY JUDGE ADVOCATE GENERAL’S CORPS ATTORNEY (27A)
- Judge Advocates are responsible for offering legal support that involves military operations. They primarily focus on the areas of criminal law, legal assistance, civil/administrative law, labor/employment law, international/operational law, intelligence law, and contract/fiscal law.
- Duty locations include the continental United States and installations worldwide such as Germany, Korea, Japan, and Italy.
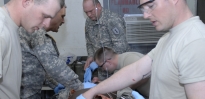
- MEDICAL CORPS OFFICER (62)
- An Army Medical Corps officer is responsible for the overall health of Soldiers and providing health care to Soldiers’ families and others eligible to receive this care in the military community.
- During combat, the Medical Corps officer oversees the emergency medical management of casualties and makes sure Soldiers are combat ready when it comes to their overall health.
- MEDICAL SPECIALIST CORPS OFFICER (65)
- Medical Specialist Corps officers are essential in treating and helping the overall health of Soldiers and their families.
- The Army Medical Specialist Corps includes four areas of specialty: Occupational Therapist, Physical Therapist, Dietitian, and Physician Assistant.

- SPECIAL FORCES OFFICER (18A)
- The Special Forces officer is the team leader of an operational detachment alpha, a highly trained 12-man team that is deployed in rapid-response situations. The officer organizes the mission, outfits the team and debriefs them on the mission objective.

- VETERINARY CORPS OFFICER (64)
- As an Army veterinary officer, you can practice in three primary areas: animal medicine, veterinary public health, and research and development. You will be responsible for treating government-owned animals and the valued pets of service members and their families.
- Army Veterinary Corps officers are also responsible for programs ensuring the safety and security of Department of Defense food supplies, both here and abroad. Approximately one-third of Veterinary Corps officers are involved in research and development in an incredible range of focus areas, from basic breast cancer research to vaccine development.
- Many times, Army veterinarians deliver public health programs around the world such as vaccination programs in Ecuador, teaching Thai veterinary technicians, or supporting foot and mouth disease eradication efforts in Mongolia