![]() Introduction
Introduction
EOH 356A – Environmental Health I Click here to start recorded
lecture.
1.
Sanitarian: a person who applies
Environmental Health
to
manage our surroundings.
(NEHA:
National Environmental Health Association)
2.
Environmental the area of public
health that studies how
Health: the environment affects human health.
CDC: Centers
for Disease Control and Prevention
(environment
<----> humans)
3.
Public a group of disciplines
devoted to the prevention
Health: of disease and the promotion of
health from the
community
perspective.
(APHA: American Public Health Association)
4.
Health: a state of complete
physical, mental, and social well
being,
and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity. __
(WHO: World Health Organization,
1948)
5.
Environment: the sum of all external
conditions and influences
in
human's surroundings, which include biological,
chemical,
physical, psychological, and sociological
hazards.
6.
Epidemiology: the study of the distribution and determinants
of disease.
a) determinants:
"causes"
b) distribution: rates:
prevalence: #
of existing cases ("sick people")
total
population
incidence: #
of new cases in a time frame
# of people exposed
__
c) disease: carcinogenesis: causes cancer
mutagenesis: causes
genetic disorders
teratogenesis: causes birth defects
7.
Interaction of contaminants:
a) synergism: 1 + 1 = 3
b) potentiation: 1 +
0 = 2
c) antagonism: 1 + 1 = 0
8. Followup:
a)
EOHSA: Environmental and Occupational Health Students Association __
b)
CEHA: California Environmental Health Association
c)
CSUN Department of EOH
/ About our Faculty
d)
NLM: National Library of Medicine
To take quiz, click here
Web address for this page
For a hardcopy printout of these pages,
go to http://www.csun.edu/~vchsc006/pages.pdf
Legal
concepts
Click here to start recorded
lecture.
Legal
databases, interview county health dept or Robert Kwong
A.
General
1. law: binding requirements imposed by
government.
(a
general term)
2. rights: a power, privilege, or interest,
protected by law.
3. duties: the corresponding responsibility to
respect a right.
4. stare decisus:
"the decision stands"
B.
Types of law (by precedence)
5. constitutional: fundamental laws of a government
includes:
federal and state constitutions,
city charters
6. statutory: laws passed by vote of legislature or
public
includes:
statutes, ordinances, referenda
7. administrative: laws written by appointed officials
(agencies)
includes:
regulations, rules
8. common: laws taken from previous court
decisions
includes:
tort law = a "private wrong"
separate from statutes
and contracts
(also
includes nuisance laws and eminent domain)
C.
Other fundamental powers
9. nuisance
laws: government may limit use of
property
if
it harms others or is "unreasonable"
10.eminent
domain: government may "take"
property if:
for
the public interest, and
fair
compensation is made
11.police
power: government must have power to
enforce its own
regulations
12.subpoena: court order for records or witnesses in
court
Legal concepts (continued)
Click here to start recorded
lecture.
D.
Responsibilities
1. malfeasance:
unauthorized (wrongful) act by an official.
2. misfeasance:
authorized act in an unauthorized manner.
3. nonfeasance:
failure to perform duty (without excuse).
4. due process:
fairness and completeness of laws
5. equal
consistency of law
protection:
6. exclusionary
evidence must be legally obtained
rule:
7. demurrer: admit
to facts but challenge legal propriety
E.
Approaches:
8. litigation: to
settle a dispute in a court of law
9. arbitration: to
settle a dispute out of court
in
a binding settlement
with
the services a disinterested person
10. negotiation: to settle a dispute out of court
in
a nonbinding settlement
between the
interested parties
11. administrative formal and informal means to gather
information
hearings: and clarify positions
F.
Other
12. NEPA: National Environmental Policy Act
(1969)
established
Council on Environmental Quality:
advise
president on environmental issues
projects
funded by the federal government require
environmental
impact statements
Population and Energy
Click here to start recorded
lecture.
A.
Population
1. Global: almost 7 billion
2. Top 5
countries:
3. 14 Mega-cities
(>10 million):
4. Demographic a theory that economic and technological
growth
leads
to a decline in death rates
followed
by a decline in birth rates
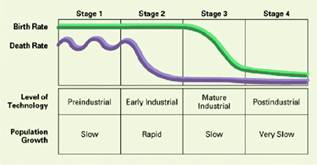 Figure 1:
Figure 1:
B.
Energy
5. Greatest use: industrial countries (
greatest less developed countries
increase: and "centrally planned
economies"
6. Non-renewable fossil fuels, nuclear power
resources:
7. Renewable solar, organics (e.g., methane),
resources:
wind,
water, geothermal;
wood,
crop residue, animal dung
Communicable Disease
Click here to start recorded
lecture.
1. communicable transmission
disease: of an agent (or its by-product)
from
reservoir
to
host.
2. agent: a factor that must be present for
a
disease
to occur in a susceptible host.
3. infection: growth of a pathogenic microbe in a
host
(with or without
evidence of disease)
(also
called "sepsis").
4. pathogenicity: capable of producing disease.
5. virulence: harmfulness of a disease.
6. reservoir: any place where an infectious agent
depends
primarily for survival.
7. host: any animal infected by an
agent;
may
be diseased or may be intermediate host.
8. incubation time interval between exposure
period: to infectious agent and first
sign
or symptom of disease.
9. carrier: person or animal that harbors an
organism
of
disease without showing symptoms.
10. asymptomatic
carrier: never shows symptoms
(also
called "inapparent infection").
11. transmission: any
mechanism by which a susceptible human
host
is exposed to an infectious agent.
12. fomites: inanimate objects (other than food,
water)
which
harbor or transmit infectious organisms.
13. vector:
insect or other animal that may transfer
pathogens
to humans.
14. infestation:
humans, lodgment, development, and reproduction
animals: of arthropods on the surface of
the
body
or in clothing.
articles, harboring or sheltering animals
premises: (especially arthropods or rodents).
Selected Airborne Diseases
Click here to start recorded
lecture.
1.
Common cold
agent: rhinoviruses, coronaviruses,
others
reservoir: human
transmission: direct contact
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7fmJxALot1E
2.
Influenza:
agent: influenza viruses (3 major
serotypes):
type
A: widespread, pandemics
type
B: local epidemics
type
C: only in sporadic cases
reservoir: human
transmission: same as cold
3.
Tuberculosis:
agent: Mycobacterium
reservoir: primarily human
transmission: primarily droplet nuclei
4. Coccidioidomycosis:
agent: Coccidioides
immitis (fungus)
reservoir: soil
transmission: airborne
5.
Pneumonia: inflammation of the
lungs with congestion
(not a specific disease, but a pathological
term
-- i.e., symptoms)
reservoir: essentially human
transmission generally direct, sometimes
airborne
various
agents:
5.
pneumococcal
pneumonia (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
6. mycoplasmal
pneumonia (Mycoplasma
pneumoniae)
7. pneumocystis
pneumonia (Pneumocystis
carinii)
8. chlamydial
pneumonia (Chlamydia trachomatis)
9. others: various viruses,
rikettsias (Q fever),
Legionella,
worms
(nematodes),
etc.
Selected Water-borne Diseases
Click here to start recorded
lecture.
1. typhoid fever
agent: Salmonella
typhi
reservoir: human
transmission: indirect, vectorborne
(flies)
symptoms: can be asymptomatic
fever,
gastroenteritis, nosebleeds
rose
spots (red patches on abdomen)
2. paratyphoid
fever
agent: 3 main groups of Salmonella paratyphi
reservoir: primarily human
transmission: same as typhoid fever
symptoms: similar to typhoid, but much less
virulent
3.
Cholera
agent: Vibrio
cholera
reservoir: human; perhaps environmental reservoirs
transmission: fecal (or vomitus)
[direct,
indirect (food, water, flies)]
symptoms: sudden and severe diarrhea
vomiting,
dehydration, death
4.
Shigellosis (bacillary dysentary)
(dysentary)
= acute colitis with diarrhea
agent: 4 groups of genus Shigella
(bacteria)
reservoir: humans; primates
transmission: fecal [direct, indirect (food, water, flies)]
symptoms: diarrhea, fever, nausea
stools
contain blood, mucus, and pus
5. Amebiasis
(amebic dysentary)
agent: Entamoeba
histolytica (a protozoon)
reservoir: human; usually a chronically ill
or
asymptomatic carrier
transmission: fecal [direct, indirect (food, water, flies)]
acute
patients pose limited danger
(absence
of cysts)
symptoms: often asymptomatic; fever, chills,
diarrhea
stools
contain blood, mucus
6. Giardiasis
agent: Giardia
lamblia (protozoan)
reservoir: human; possibly other animals
transmission: fecal
(water or food) (cysts resist treatment)
symptoms: often asymptomatic; diarrhea, cramps,
fatigue
Selected Helminthic Diseases
Click here to start recorded
lecture.
1.
Trichinosis
agent: Trichanella
spiralis
reservoir: pigs, wild boar, bears, foxes, wolves,
rats
transmission: eating infected animals
symptoms: nausea, gastroenteritis
(must
thoroughly cook pork >150 deg. F)
2. Ascariasis (roundworms)
agent: primarily Ascaris
lumbricoides
reservoir: humans, infected soils
transmission: not person to person
ingestion
of infective eggs (soil)
symptoms: live worms in stool
varied:
coughing, fever, nutrition
3. Schistosomiasis (blood flukes)
agent: Schistosoma
(4 species)
reservoir: humans (and various animals)
transmission: vectors (biological)
larvae
from snail infested waters
symptoms: varied
4.
Other helminthic diseases
a. beef
tapeworm Taenia
saginata
b. pork
tapeworm Taenia
solium
c. fish
tapeworm Diphyllobothrium
latum
d. dracunculiasis
(dracontiasis) Dracunculus
medinensis
e. ancylostomiasis
(hookworm) Ancylostoma
f. enterobiasis
(pinworm) Enterobias
Selected Miscellaneous Diseases
Click here to start recorded
lecture.
1.
Ringworm
agent: Microsporum, Trichophyton, others (fungi)
reservoir: infected human or animal
transmission:
physical contact
symptoms: dermatitis (athlete's foot,jock
itch, etc.)
control:
cleaning floors, showers, clothing
2.
Tetanus
agent: Clostridium tetani
reservoir: soil, street dust, animal feces
transmission:
entrance in a wound
symptoms: muscular contractions, spasms
case
fatality can be high
control:
immunization, cleansing wounds
3.
Anthrax
agent: Bacillus anthracis
reservoir: cattle, sheep, goats, horses, swine
transmission:
contact with hides or meat, flies
symptoms: itchy skin; complications if untreated
control:
vaccine, sanitation, dust control
4.
Leprosy
agent: Mycobacterium leprae
reservoir: humans
transmission: not
clearly established
prolonged
contact is important
symptoms: disease of skin, nerves, nasal musosa
symptoms
vary
Selected Food Related Illnesses
Click here to start recorded
lecture.
A.
Infections
1. Salmonellosis Salmonella typhimurium
Salmonella enteritidis
2. Campylobacter Campylobacter
jejuni
3. Listeriosis Listeria
monocytogenes
4. Hepatitis type A = infectious
5. Brucellosis Undulant Fever
6. Trichuriasis Trichuris
thrichiura
7. Anisakiasis Anasakidae
family
B.
Intoxications
8. Staphyloccoccus
Staphyloccoccus aureus
9.
Botulism Clostridium botulinum
10. Perfringens Clostridium perfringens
C.
Poisonous plants/animals
11. Favism Vicia
faba
12. Snake root Eupatorium
13. Paralytic
shellfish
poisoning
14. Ciguatera
15. Scombroid Scombridae
family
D.
Others
16. agent: Vibrio
parahemolyticus
reservoir: oceans (variety of seafood)
transmission: poorly cooked seafood
symptoms: diarrhea, abdominal cramps (rarely
fatal)
17. agent: Bacillus cereus
reservoir: soil
transmission: especially cooked rice at room
temperatures
symptoms: sometimes vomiting, sometimes
diarrhea
18. agent: Clostridium perfringens
(anaerobic sporeformer)
reservoir: soil; also, GI tract of healthy humans or
animals
transmission: spores survive normal cooking,
then
germinate, multiply, and produce toxins
symptoms: diarrhea, nausea; usually no vomiting or
fever
19. agent: Copper poisoning
transmission: copper in prolonged contact with acid foods
or
carbonated
beverages
(e.g., improper vending
machines)
symptoms: vomiting and weakness in < 1 hour
(often minutes)
Food Controls
Click here to start recorded
lecture.
A.
Pasteurization:
1. Ultra Pasteurization: >280 deg. F for >2 seconds
2. Ultra High Temperature: 191-212 deg. F.
for 1 to .01 seconds
(UHT)
3. High Temp. Short Time: 161 deg. F for 15 seconds
(HTST)
4. Holder pasteurizer: 145 deg. F for 30 minutes
B.
Food and Temperatures:
5. Thermometers: required in refrigerators.
should be: readily visible
at the warmest part of the unit
accurate to 1 degree Centigrade
6. Stem designed to check food
temperatures
(or probe) typically has metal stem
thermometer: with temperature readings at top of
thermometer
Restaurant operators must have on the
premises.
7. Maximum used to check temperatures in
dishwashing machines
registering
thermometer:
8. Refreezing: frozen foods may not be thawed and
refrozen
(exception:
when food is cooked or processed
after
thawing).
Click here to start recorded
lecture.
C.
Canning operations:
1. soaking reduces spoilage bacteria
and
washing:
2. sorting consistent quality of product
and
grading:
3. blanching: direct contact with hot water or steam
destroys
enzymes (reducing chemical changes)
softens
tissues to fit in can
washes
away "raw" flavor
4. exhausting: heat foods in cans prior to closing can
produces
partial vacuum
5. sealing: secures lid on can
hermetic
double seam
when
can cools, lids pull in (concave)
6. retort closed vessel for
"sterilization" of food
processing: 240 degrees for 30 minutes
7. cooling: quick cooling minimizes thermophilic bacteria
potential
for water contamination through seams
(water
must be disinfected)
D.
Dishwashing:
8. Manual 3 compartment sink:
method:
detergent and warm
water:
good
at removing, not killing bacteria
most
important step in dishwasing
rinse:
removes detergent before sanitizer
sanitizer:
a
"polishing" step
hot
water (180 deg F, 30 seconds)
chemicals
and warm water (75 deg F):
chlorine: 100 ppm for 30
seconds
quaternary
ammonia: 200 ppm
for 1 minute
iodine: 25 ppm for 1
minute
9. Machine see NSF
standards
method: (National Sanitation Foundation)
wash: 140-160 deg. F
rinse: 180 deg F,
10 seconds, 15-25 psi (water
pressure)
or
chlorine rinse (50 ppm)
HACCP = Hazard Analysis and Critical Control
Point
Click here to start recorded
lecture.
developed by
Pillsbury Company for NASA astronauts in 1960s
since then, adopted
by FDA, USDA, and Dept. of Commerce
predicts hazards
and controls them before they happen
1.
Identify hazards
(i.e., biological, chemical, and physical
hazards)
identify
potentially hazardous foods
assess risk
(e.g., high, medium, low, negligible)
2.
Identify critical control points
def. = any point in an operation where
the hazard can be
eliminated,
prevented, or minimized
observe the
handling of food throughout its lifetime
identify:
sources of contamination, and
potential
for microbes to survive or grow
3.
Establish controls
identify:
control criteria (e.g., temperatures)
corrective
action
4.
Monitor
monitor the critical control points
record the data
5.
Establish corrective action
take action when
criteria are not met
6.
Verify that HACCP is functioning
CURFFL
=
Articles 1-17 (containing
sections 27500-27863)
Articles
1. general provisions 9. open
air barbecue facilities
2. definitions 10. vending
machines
3. plan review and permits 11. vehicles
4. enforcement and inspection 12. mobile
food preparation vehicles
5. permit suspension / revocation 13. temporary food
facilities
6. general sanitation requirements 14. produce
stands
7. sanitation requirements for 15. certified
farmer's markets
food
facilities 16. satellite food distribution
8. sanitation requirements for 17. restricted
food service transient
food
establishments
occupancy establishments
Commercial Food Protection:
Who does what in the federal government?
Click here to start recorded
lecture.
A.
hopelessly 35 laws
fragmented:
12 agencies
51 interagency agreements
(not
counting federal-state
interagency
agreements)
B. 6
major 1. Food and Drug
Administration (FDA)
agencies:
2. Environmental Protection
Agency (EPA)
3. National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS)
4. Food Safety and Inspection
Service (FSIS)
5. Agricultural Marketing
Service (AMS)
6. Federal Grain Inspection
Service (FGIS)
C.
funds: USDA receives about 3/4 of
federal funds
FDA is second, with about 1/8
of federal funds
D.
FDA 1. Food Drug and Cosmetic
Act
major
laws: 2. Egg Products Inspection Act
3. Federal Anti-tampering Act
4. Import Milk Act
5. Infant Formula Act
6. Pesticides Monitoring
Improvements Act
7. Public Health Service
Act
Selected Food Additives
Click
here to start recorded
lecture.
1.
DES: Diethylstilbestrol
synthetic
estrogen
used
to fatten cattle and chickens
effects:
carcinogen, mutagen
FDA banned in 1977
2. sodium illegal
to mask food
nitrite: interferes with browning of meat:
myoglobin + sodium nitrite --> met-myoglobin
deters
spoilage and botulism in cured meats
effects:
headaches or hives in sensitive persons
nitrites
--> nitrosamines (carcinogen)
however:
not a direct additive
no
evidence of increased cancer
nitrates
reduce to nitrites inadult saliva
(nitrates
found in spinach, celery,
lettuce,
etc.)
3. monosodium (MSG,
flavor enhancer, natural flavoring,
glutamate: hydrolyzed vegetable protein)
effects: headaches, nausea, diarrhea,
burning
sensation, chest pain, etc.
brain
lesions in monkeys and mice
4. aspartame: only in
sensitive persons (phenylketonurics)
effects:
swelling of eyelids, lips, hands, or feet
5. sulfites: effects:
abdominal cramps, diarrhea,
low
blood pressure, elevated pulse,
light
headedness, chest tightness,
asthma,
hives
FDA banned use on raw fruits
and vegetables
FDA requires labels when more
than 10 ppm
Selected Arthropod Pests
Click
here to start recorded
lecture.
A.
arthropods: insects (roaches, fleas, flies,
mosquitoes, lice)
arachnids
(ticks, mites, spiders)
others (myriapods,
diplopods,
crustaceans)
Insect
Pests
B.
Roaches:
1. American Pareplaneta
cockroach: large (about 1.5 inches)
reddish
brown
2. Oriental Blatta
orientalis
cockroach: about 1 inch
brown
or black
3. German Blatella
germanica
cockroach: medium (about 1/2 inch)
light
brown
4. Brown-banded Supella
longipalpa
cockroach medium (about 1/2 inch)
light
brown with darker
brown
bands across abdomen
C.
Fleas:
5. Cat Flea:
Ctenocepalides
felis
not
normally a vector
6. Dog Flea: Ctenocepalides
canis
not
normally a vector
7. Oriental Xenopsylla
cheopis
Rat Flea: spreads plague, etc.
Selected
Arthropod Pests (continued)
Click here to start recorded
lecture.
Insect
Pests (continued)
D.
Flies:
1.
House fly: Musca domestica
2.
Lesser Fannia
House fly:
3.
Stable fly: Stomaxys
4.
Bottle fly: Caliphora
(or Blow
fly)
5.
Flesh fly: Sarcophagidae
6.
Horse fly: Tavanus
(or gadfly)
7.
Vectors: Tsetse fly: Glossina
Black fly: Similium
8.
Ash whitefly: not a true fly
(related to aphids)
waxy coating
prevents
absorption
of insecticide
no
natural enemies in
E.
Mosquitoes:
9.
Anopheles: transmits
malaria
Anopheles quadrimaculatus
Anopheles albimanus
Anopheles freeborni
10. Culex: Culex
pipiens
Culex
tarsalis
11. Aedes: Aedes
aegypti
Aedes
albopictus
F.
Lice:
12. head lice: Pediculus
humanus capitis
13. crab lice: Pthirus
pubis
pubic
lice
14. body lice: Pediculus
humanus corporis
a
major vector
Selected
Arthropod Pests (continued)
Click here to start recorded
lecture.
Arachnid
Pests
A.
Ticks:
1. hard ticks: Ixodidae:
Ixodes
dammini
Ixodes
pacificus
Dermacentor
andersoni
Dermacentor
variabilis
2. soft ticks: Argasidae:
Ornithodoris
hermsi
Ornithodoris
coriaceus
B.
Mites:
3. chiggers: larval stage
C.
Spiders:
4. black
widow
5. brown
recluse
Selected
Insect-borne diseases
Click here to start recorded
lecture.
1. Onchocerciasis
(river blindness)
agent: Onchocerca
volvulus (nematode, or roundworm)
reservoir: mostly humans
transmission: bite of infected female blackfly
(genus
Similium) biological vector
symptoms: chronic, nonfatal (incubation 1 year
or more)
intense
itching, impaired vision
A.
mosquito-borne
2. human
malarias
agent: Plasmodium
reservoir: human, infected mosquitoes
transmission: anopheles mosquites
symptoms: fever, chills, sweats
CNS effects (headache,
delirium, coma)
3. filariasis
agent: Wuchereria,
Brugia (nematodes, or roundworms)
reservoir: humans
transmission: mosquitoes (Aedes,
Anopheles, and Culex)
symptoms: asymptomatic; fever, asthma
elephantiasis
in chronic cases (enlarged limbs)
4. yellow
fever:
agent: yellow fever virus (a flavivirus)
reservoir: humans (sometimes monkeys) and
mosquitoes
transmission: Aedes
mosquito
symptoms: sudden onset, fever, jaundice
headache,
backache, vomiting
5. dengue (breakbone) fever
agent: Dengue virus
reservoir: human, infected mosquitoes
transmission: Aedes
mosquitoes
symptoms: headache, joint and muscle pain,
rash
6. Arthropod-born viral encephalitis
agents: Eastern equine, Western
equine,
reservoir: unknown for most agents
(possibly
birds, rodents, bats, reptiles)
transmission: Culex
mosquitoes, possibly Aedes and others
symptoms: often asymptomatic
inflammation
of brain, spinal cord, meninges
headache,
fever, convulsions, paralysis, coma
Selected
Arachnid-borne diseases
Click here to start recorded
lecture.
A.
Tick-borne
1. Rocky mountain spotted fever
agent: Rickettsia
rickettsii
reservoir: dogs, rodents, other animals
transmission: infected ticks (various species)
symptoms: fever, headache, malaise, chills,
rash, death
2. Tularemia
agent: Francisella
tularensis
reservoir: wild animals (rabbits, muskrats)
transmission: bite of flies or wood ticks,
handling
or ingestion of infected animals
symptoms: typically: swollen lymph nodes,
gastroenteritis
3.
agent:
reservoir: small animals (squirrels, chipmunks,
porcupine)
transmission: infected ticks: Dermacentor
andersoni
symptoms: similar to Dengue fever
4. Q fever
agent: Coxiella
burneti (rickettsia)
reservoir: ticks, various wild and domestic
animals
transmission: raw milk from infected cows, or direct
contact
symptoms: typically: chills, headache
5. Relapsing fever
agent: Borrelia
recurrentis (spirochete)
reservoir: louse-borne: human; tick-borne: rodents
transmission: lice or tick bites
symptoms: rash, fever
B.
Mite-borne
6. Scrub typhus
agent: Rickettsia
tsutsugamushi
reservoir: infected larval mites, wild
rodents
transmission: mite bites
symptoms: skin ulcer at site of bite,
headache
7. Scabies (sarcoptic
itch, acariases)
agent: Sarcoptes
scabiei (a mite)
reservoir: humans
transmission: skin to skin, mites can burrow in < 3
minutes
symptoms: itching, lesions
Selected
Zoonoses
Click
here to start recorded
lecture.
1. Zoonoses:
diseases and infections transmitted between
vertebrate animals
and humans
2.
Plague:
agent: Yersinia
pestis
reservoir: wild rodents and infected fleas
transmission: mainly flea bite (especially Xenopsylla cheopis)
sometimes
person to person (respiratory)
symptoms: swollen lymph nodes, fever,
pneumonia
3. Murine typhus fever (or endemic typhus):
agent: mainly Rickettsia
typhi
reservoir: rodents, fleas, opossum
transmission: bite or feces of rat flea (Xenopsylla cheopis)
symptoms: headache, chills, fever
4. Leptospirosis:
agent: Leptospira
interrogans (a spirochete)
reservoir: farm animals and pets;
usually
rats and other rodents
transmission: contact of skin with water, soil or
vegetation
contamination
by urine
symptoms: may be asymptomatic,
fever,
headache, chills, malaise, vomiting
5.
Psittacosis:
agent: Chlamydia psittaci
reservoir: birds (pigeons, parrots,
parakeets,
turkeys,
ducks)
transmission: airborne (inhaling dried droppings)
person
to person is rare
incubation
4-15 days (usually aabout 10 days)
symptoms: varies (fever, headache, chills,
sometimes cough)
6.
Rabies:
agent: rabies virus
reservoir: 1. skunks 2. bats
and racoons
3. foxes 4. dogs,
cats, cattle
transmission: mainly animal bites, or licks on
wounds
rarely:
scratches, airborne, person to person
symptoms: incubation period: 2-8 weeks
fever,
paralysis
untreated,
almost always fatal
Selected
Insecticides
Click
here to start recorded
lecture.
A.
inorganic:
1. Boric acid powder
2. Sodium fluoride
3. Paris Green: arsenic trioxide + copper acetate
4. Silica gel (SiO2): a dessicant
B.
botanicals:
"natural" pesticides
5. Pyrethrum from chrysanthemums, often used with
(and pyrethroids): a
synergist (piperonyl butoxide)
6. Rotenone roots of Derris plant (legume)
(and rotenoids):
dusting powder for ticks on animals
7. Nicotine: usually nicotine sulfate
C.
chlorinated
hydrocarbons: usually low toxicity, but
persistent
8. DDT: dichloro
diphenyl trichloroethane
9. others: mirex, endrin, dieldren, chlordane, BHC,
heptachlor,
toxaphene
D.
organophosphates: usually low persistence, high toxicity
acetylcholinesterase inhibitor
10. Parathion,
Malathion
11. DDVP (Dichlorvos)
Diazinon
E. carbamates:
also an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor
12. Carbaryl (Sevin)
Aldicarb
Selected
Rodenticides
Click
here to start recorded
lecture.
A.
anticoagulants: multiple doses kill
by internal bleeding
1. warfarin
2. others: pival, fumarin, PMP, diphacinone
B.
botanicals:
3. Red squill: (from the plant)
natural
emetic (causes vomiting)
4. others bay leaves, cucumber skins
C.
quick kill: extremely
toxic
5. 1080 (Sodium Fluoroacetate)
1081 (Sodium Fluoroacetamide)
only
for registered pest controllers
6. others: Strychnine, Zinc phosphide, cyanide gas
ANTU (alpha naphtyl thiourea)
D.
selective: toxic to Rattus genus
7. Norbromide: vasoconstrictor
______________________________________________________________
8. evidence of droppings,
burrows
rodents: gnawing marks (wood, cement, wires,
etc.)
urine (shiny streaks
under blacklight)
greasy
runways (especially Rattus norvegicus)
9. other first, kill fleas (ectoparasite)
rodent
controls: cement or steel curtains
around house
to
prevent burrowing
traps
(traditional, or adhesive)
Pest
Control
Click here to start recorded
lecture.
A.
Alternative Pests Controls:
1. quarantine
2. antifeedants/ irritants to surface feeding insects
repellants: no feeding = starvation (e.g.,
pyrethrum)
3. natural birds, spiders
predators: bacteria, viruses (e.g., Bacillus thuringiensis)
Gambusia
affinis (eats mosquito larvae)
4. agricultural irrigation
(e.g., minimize standing water)
practices: rotate crops (some crops are naturally
resistant)
destroy
crop residues (reduces food for pests)
5. natural
pesticides: (e.g., botanicals)
6. resistant
crop
strains: (genetic engineering)
7. pheromones: sex attractants:
confuses
males in locating females
only
minute amounts needed (low toxicity)
complements
the use of pesticide
8. juvenile internal chemicals that regulate
growth
hormones: (e.g., eggs hatching to nymphs)
if
we can synthesize juvenile hormones:
altered
concentration = no development
low
toxicity
difficult
for pests to develop resistance
9. autocide: insect sterilization (usually U.V.
radiation)
sterile
males mate with fertile females
most
effective when pest population is low
complements
chemical methods (which are more
effective
when pest population is high)
B.
Laws:
10. FIFRA (1947): Federal Insecticide,Fungicide, and Rodenticide
Act
registers
pesticides, requires testing
11. FEPCA (1972): Federal Environmental Pesticides Control
Act
allows
EPA to regulate pesiticides
12. ToSCA
(1977): Toxic Substances Control Act --
allows EPA to:
require
information from chemical manufacturers,
test
new chemicals for
environmental
and health effects,
regulate
chemicals not addressed by other laws.
Click here to start recorded
lecture.
A.
Solid discarded material (EPA definition)
waste:
includes:
solids, liquids, contained gases
excludes:
agricultural wastes returned to soil
mining
and milling wastes returned to mine
domestic
sewage, and nuclear materials (!)
1. garbage: relatively decomposable wastes
(kitchen,
food wastes)
2. rubbish: relatively non-decomposable wastes
(paper,cloth,
glass, metal)
B.
phases: input process output outcome
generation
--> transfer --> disposal --> effects
| | | |
source resource remediation |
reduction recovery compensation
3. collection: greatest cost of solid waste
management
4. transfer: temporary holding facilities
(for
collection, storage, some treatment)
5. treatment: to reduce volume, mass, or risk
6. incineration:
controlled combustion of waste
7. RDF: refuse derived fuel (waste is
incinerated)
8. mass
burn: nothing is sorted
9. controls: temperature (1400-1800 degrees F.)
turbulence
(oxygen) -- grates:
rectangular,
vertical circular,
rotary
kiln, others
time
(continuous preferred over batch)
10.ash: solid residue that remains after
burning
(bottom
ash = at bottom of incinerator)
(fly
ash = smaller airborne particles)
11.pyrolysis: burn wastes with no added oxygen
("roasting")
Solid
Waste (continued)
Click
here to start recorded
lecture.
12. composting: controlled biodegradation of
plant
and animal matter
13. humus: decomposed plant and animal matter
soil
conditioner (poor fertilizer)
14. windrows: long rows of compost
15. procedure: shred (allows faster decomposition)
spread
in thin layers (2"-6"):
carbon
layers: paper, leaves, sawdust
nitrogen
layers: grass, kitchen scraps,
fruit
activator
layers: manure (dog droppings, etc.)
soil
fertilizer
sprinkle with water
to maintain moistness
ventilate
16. problems: AVOID:
meat, grease, bones, and weeds
odor:
if ammonia smell, add carbon
if rotting smell, add carbon,
ventilate,
stop watering
if
too slow: add nitrogen, activator
maintain water and oxygen
17. resource
any process where materials are recovered
recovery: rather than discarded
18. reuse: use
again in same way
19. reclamation:
(utilization) use in new ways
20. recycling: use raw
material in various ways
(e.g., cullet = ground
glass)
21. source to
re-evaluate and eliminate waste generation
reduction:
22. tipping fees:
charge to dump garbage at a
disposal
site ($/ton)
Page 44: Sanitary Landfills Click here
to start recorded lecture.
A.
Features:
1. protective clay soils or
lining: synthetic liners (PVC, PE)
2. layers 8-10 ft. deep (after compaction)
(lifts): intermediate settling (prefer 1
year)
before
next lift
3. cover daily: 6 inches
material: intermediate: 12 inches
final
cover: 24 inches
2-4 % grade
(for proper drainage)
less than 30 degrees on side slopes
B.
Methods:
4. area: uses
natural slope: valley or ravine methods
low area method
ramp method
5. trench: man-made
C.
Processes:
6. LFG: landfill gas
aerobic: a. lasts several days to several
months
anaerobic: b. mostly CO2 formation (acid formers)
c.
increased methane formation (methane producers)
d.
stabilized (roughly equal % of methane and CO2)
(lesser levels of NH3 and H2S)
rates: depend on temperature, pH (acid
inhibits growth),
moisture,
type of wastes
methane: explosive limit of 5%
7. Leachate: from waste itself,
or water entering landfill
high
in organics, heavy metals
D.
Daily concerns:
8. records: type and amount of waste received
(measure
by weight, because volume changes),
# and
type of personnel, equipment
monitoring
leachate and gas production
9. procedures: standby equipment
exposed
waste area is minimized
work
with prevailing wind
portable
fencing (prevent wind blown waste)
compact
to 12-18 inch layers (4-5 passes of tractor)
E.
Long-term concerns:
10. space: land area needed
11. access: fences, signs
12. time: 20-40 years operation
Page 45: Defining "Hazardous Waste" Click here to start recorded lecture.
production environment waste
|--> hazardous air
pollutants -->|
| [Clean Air Act (CAA)] |
| |
toxic
---------->|--> toxic pollutants ---------->|--> hazardous
substances |
[Clean Water Act (CWA)] | wastes
(TSCA) | | (RCRA)
|--> hazardous
substances ------>|
| (CWA, RCRA, CERCLA) |
| |
|--> hazardous materials
------->|
(HMTA)
II. Under RCRA
A. "D-Wastes": exhibit at least one of
four
characteristics:
1. ignitibility:
flash point < 140 deg. F.
2. corrosivity: pH < 2, > 12.5, or
corrode
steel at > 1/4 inch per year
3. reactivity: explosiveness and toxic by-products
from
chemical reactions
4. toxicity: standard extraction procedure (EPA)
B. any of four lists (created by EPA, and
taking
precedence over the above characteristics):
5. F-list: from generic processes
e.g., degreasing,
solvents, electroplating
6. K-list: by type of industry:
e.g., iron and steel,
petroleum refining
pesticides,
explosives
7. U-list: "toxic wastes" (numerous
qualifications)
8. P-list: "acutely hazardous"
presents
substantial hazard
whether
improperly managed or not.
C. Mixtures of solid waste with waste
listed above
D. Waste from the treatment, storage, or
disposal (TSD)
of wastes
listed above
Acronyms
Click here to start recorded
lecture.
A.
General Considerations
1. DOT:
Department of Transportation
2. HMTA:
Hazardous Materials Transportation Act (DOT)
3. HCS:
Hazard Communication Standard (OSHA)
4. CHEMTREC:
(1-800-424-9300)
5. CMA:
Chemical Manufacturers Association __
B.
RCRA and HSWA
6. SQG:
small quantity generators (below legally
prescribed
quantities, generators are subject
to
less stringent RCRA requirements)
7. HSWA:
Hazardous and Solid Waste Amendments
of
1984 (to RCRA)
C.
CERCLA
8. RQ:
Reportable Quantity (under CERCLA, releases above __
this
level must be reported to the national response
center,
a toll free hotline at 1-800-424-8802).
9. NCP:
National Contingency Plan
10. CERCLIS:
Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation,
and
Liability Information System (an inventory,
often
a prelude to being placed on NPL)
11. HRS:
Hazard Ranking System
12. NPL:
National Priorities List (based on HRS) __
D.
SARA
13. ATSDR:
Agency for Toxic Substance and Disease Registry
14. EPCRA:
Emergency Planning and Community Right to Know Act
(title
3 of SARA)
15. TPQ:
Threshold Planning Quantity (under SARA,
releases
above this level must be reported
to
the State Emergency Response Commission).
16. TRI: Toxic Release Inventory