Who will
pay for the AAC Device? Once it
has been ascertained that a client (child or adult) will benefit from AAC
services, and a proper device as been identified, the matter of itÕs cost
becomes a leading issue. This was
not the case in the selection of the device. In that process, the matching of the correct device to the
userÕs needs was the primary concern.
But in most cases, the cost of the selected device exceeds the userÕs
ability to pay. There are,
however, a number of funding sources that can be explored by the AAC Team, led
typically by the Speech Pathologist.
The hierarchy of sources includes the following: Private
Purchase; CCS and MediCal; CCS alone;
MediCal alone; Private Insurance;
Low Incidence Education Funds; and General Education Funds, and many
philanthropic organizations.
1. Private Purchase: When feasible, there are important
advantages to be gained if the device can be purchased directly by the client
or his/her caretakers using their own funds.
a. The Time Advantage: In a private purchase, the process, and
hence the time it takes to actually
procure the device, can be significantly shortened. This reduced time can be a
critical issue, for example, in the case of ASL patients where the need for the
device is great and immediate but frequently short lived; or in the case of
young children where every day without the device may result in a significant
loss of opportunity to learn basic communication skills.
b. The Ownership
Advantage: Additionally,
when users purchase their own device, it is clearly their property and can go with them when they move. This is not the case when the funding
comes through the schools, for example, who then have the say as to when the
device can be taken off campus (for example home
after school); and to whom the device must be returned if the child moves
out of the District.
c. The Accessories
Advantage: There are many desirable features associated with AAC
devices that may be excluded by many insurance sources, but which can be
included if the device is privately purchased. For example, word processing and similar applications,
access to the Internet, and many games are not allowed by many insurance programs
but can be purchased privately.
2. California Children Services (CCS) and
MediCal, for Children in need of an AAC Device: When the AAC funding for a child is
dependent upon various government or private agencies, the organization of choice is a combination of CCS and MediCal.
a. MediCal is California's version the Medicaid program. This is a public health
insurance program which provides needed health care services for low-income
individuals including families with children, seniors, persons with
disabilities, foster care, pregnant women, and low income people with specific
diseases such as tuberculosis, breast cancer or HIV/AIDS. MediCal is
financed equally by the State and Federal governments.
For Clients to be eligible to apply for MediCal funding, they must first
be receiving services from a Regional Center. In this regard, it is important to get the name/number of
the Regional Center Case Manager. This information can usually be
obtained from the clientÕs parents or caretakers. If MediCal Insurance has not yet been secured, it will be
necessary to ask the Regional Center Case Manager to apply for Medical Insurance for the client through Institutional
Deeming with parent approval.
To
be eligible for MediCal Insurance, the client must have more than one
handicapping condition (viz., motor, cognitive and sensory); and must be
receiving a minimum of two services
from the Regional Center. A person
over 18 years would also be eligible.
In all cases the SGD must be accepted as being medically necessary. To be eligible for a device, the client must
have a doctorÕs prescription and an evaluation by a Speech Pathologist.
A
medically necessary need is one in
which the client cannot meet daily communication needs through other means
(vis., oral speech or no or low tech AAC interventions); and one in which the SGD has been determined to
be the most appropriate means of meeting daily functional communication goals. MediCal
will help to finance doctors services, physical and occupational therapies and
medical equipment. AAC devices are
included as DME (durable medical equipment). This also includes repairs and
replacement of Devices although typically there is a five year hiatus for replacing devices. This must certainly be taken into
consideration by the SLP when selecting a device that may need to meet the
developing communication needs of a childÕs over five years; or the decline in
communication abilities associated with degenerative pathologies.
If
a client does not qualify for CCS, then MediCal may finance the AAC directly.
b. CCS is a
Statewide program managed by the California Department of Health Services. It is funded by State, County and
Federal tax monies; and some fees paid by the parents.
To be eligible for CCS funding, a child must be under 21 and
have a physically disabling condition such as cerebral palsy, muscular
dystrophy or some other medical condition which requires medical, surgical or
rehabilitative services. The
adjusted gross income of the parents must be, at least at the present, under
$40,000, or if the medical expenses must come to more than 20% of the family
income. To be eligible for a
device, the client must have a doctorÕs prescription and an evaluation by a
Speech Pathologist.
CCS will pay for the evaluation to determine whether or not
a child is eligible for their services, which include among others, doctors
services, physical and occupational therapies and medical equipment. AAC devices are included as DME
(durable medical equipment). As with MediCal, This includes purchase, repairs
and replacement of devices, although typically there is a five year hiatus for
replacing devices. This must
certainly be taken into consideration when selecting a device that may need to
meet the potential of a childÕs development over five years; or the decline
If a client is not eligible for MediCal, then CCS may
directly fund the AAC device.
c.
The Process of applying for CCS /MediCal Funding begins with
determining the status of the client with CCS and MediCal.
If a CCS status has not yet been determined, then it may be
necessary to have the parents apply for CCS Services. As was mentioned earlier, CCS will pay for an
evaluation. If, on the other hand,
the clientÕs status has become inactive,
it may be necessary (with the parents permission) to schedule an evaluation
with CCS to activate the status. If the status with CCS is at a Consultation level, or active with a CCS Medical Therapy Unit (MTU),
then it is necessary to obtain the name
and number of the Occupational Therapist, and the name and number of the Supervising
Occupational Therapist for the MTU.
If the MediCal status has not yet been determined (i.e., the
client has no MediCal Insurance), the parents should be advised about the
benefits of applying to MediCal.
Of course this depends on the clients status with the Regional Center. If the client is receiving services
from the Regional Center we will need to get the Name and Number of the Case Manager. It will be this Case Manager who will file the
application for MediCal through a process called Institutional Deeming
with parent approval.
If the MediCal application is in process, then we will proceed
with the required device funding evaluation (i.e., using the CCS/MediCare
Guidelines.) If or when the Client
has an active status with MediCal, they will be assigned an Active
Medical Number. The next
step will be to conduct a CCS/MediCal device funding evaluation. If the clientÕs status with CCS is
active, it is advisable to involve the CCS OT in the evaluation and
trials. We should take care to
follow the CCS/MediCal AAC device funding process, and provide CCS with an Evaluation
Packet.
The AAC Evaluation
Packet includes the following items:
a. The Completed AAC Device Evaluation
Report in Medicare Format.
b. The Primary PhysicianÕs Prescription
for the device and peripherals.
c. A Price Quote from a vendorized DME
Device Company delineating all equipment needs/current prices and not more than
30 days old.
d. If the Client has a Primary
Insurance Carrier, a letter of denial for funding will be
included.
3.
MediCal only for funding Children in
need of an AAC Device:
Clients who do not have a diagnosis
that is eligible for CCS (such as
Downs Syndrome, Autism or Pervasive Developmental Disorder, etc.) may be funded
directly from MediCal if they are qualified. It must first be ascertained, however, whether or not the
AAC device can be funded by the clientÕs Private Primary Health Insurance
Provider. This involves contacting
the clients Primary Health Physician to inform him/her of the evaluation. The Physician should then be provided
with the evaluation and the specifics for the prescription based on the
evaluation. The Evaluation Report;
the prescription, and the Device costs quote must be submitted and reviewed by
the Primary Health Insurance Carrier (usually by the Durable Medical Equipment
(DME) Department). If the request
for funding is approved, then the AAC device will be procured by the Private
Insurance Company. If not then a letter of denial must be provided to
the SLP. Then the Evaluation Packet (including the AAC
Evaluation Report: the Primary PhysicianÕs prescription, the Denial letter from
the Private Health Insurance Company; and the Price Quotes is sent to the Funding Department of the Device Vendor
(who must have a DME Vender Number) for MediCal.
CCS only for funding Children in need of an
AAC Device: For children
who are active or who qualify for CCS but are not eligible for MediCal,
the funding my be provided by CCS alone. The CCS status must first be
determined. Plus to be eligible
for device funding the yearly income of the parents must be below $40,000 a
year. If the child is equipment
eligible under CCS then the AAC Device Evaluation should be undertaken. The CCS OT should be notified and involved
in the evaluation process. The
completed Evaluation Packet should then be submitted to CCS.
4. Private Insurance funding for Children
in need of an AAC Device: It must first be determined whether or not the Insurance
Policy covers Speech/Language, and Durable Medical Equipment. Even so, it must also be checked to see
that there is no exclusion clause specifically for AAC Devices. An AAC Device Evaluation following
Medicare Guidelines can then be conducted. A copy of the report should be sent
to the Primary Physician including the specifics for a prescription. The Physician should then submit the funding
materials to the DME Department of the Insurance Company with a 30 day response
request. It is important to keep
touch with the parents and the Physician until a decision by the insurance
company is made. If the funding
request is denied, but the insurance does cover Speech/Language and DME, then
the objections should be ascertained and addressed and the funding request
re-submitted.
5. Low Incidence Public School funding for
Children in need of an AAC or AT Device: A child who has a low incidence disability, as
described by the State Department of Education, which includes severe
orthopedic impairments (such as cerebral palsy,) or multiple motor, speech and
sensory impairments; but who is NOT eligible for CCS, MediCal or Private
Insurance services, my apply for funding through the Department of Education. It is important in this case that the IEP Team write goals and objectives that
include the use of an AAC (or AT) device.
The next step is for the AAC Specialist and the Case Manager to complete
the Low Incidence Form and submit it
along with the EIP report to the appropriate school Program Administrator for
review. If approved, the low
incidence equipment is logged into the low incidence database and the AAC
Specialist and/or the Case Manager is contacted. When procured, the equipment is the property of the school
and will be retained by the School if the Child moves out of the jurisdiction
of the California State Department of Education. The school authorities also determine whether or when the
child can remove the AAC device from the school premises (for example to take
it home after school).
6. General Education Public School funding
for AT or AAC Equipment Budget: If a student does not qualify for low incidence funding, nor
CCS or MediCal, and Private Insurance is not an option, General Education
funding is a possibility. To
access this funding, the client must have an AAC device assessment conducted in
accordance with the Medicare guidelines.
The IEP Team must write goals/objectives, which include the use of AAC
or AT. The AAC/AT Specialist and
the Case Manager will complete an Equipment Requisition and send it along with
the IEP to the appropriate Program Administrator for review/approval. If approved the AAC/AT equipment is
logged into the equipment database and the AAC Specialist/Case manager is
contacted to obtain the equipment.
7. Tricare funding for AT or AAC Equipment
Budget: Tricare is the Insurance Carrier
for Personnel on Active duty, and their dependents. The process for applying for Tricare funding is the same as
applying to any Private Insurance Company. Medicare guidelines should be followed in the assessment
process.
8. Medicare funding for AT or AAC
Equipment Budget: Medicare is a social
insurance program administered by the United States
government, providing health insurance coverage to people who are aged 65 and over, or who meet other
special criteria. Medicare operates as a single-payer
health care system. Single-payer
health insurance collects all medical fees and then pays for all services
through a single government (or government-related) source. To obtain Medicare funding, you obtain
the aid of the Funding Coordinator of the Company Manufacturing the
Device. If the device is accepted
for funding, there is a 20% copayment required from the patient.
9. Department of Rehabilitation funding
for AT or AAC Equipment: When students are 18 years and
over, the Department of Rehabilitation Counselor should be contacted to
ascertain the possibility of obtaining an AAC/AT device that would enable the
client to achieve a vocational goal.
10. Other Organization often accessible for
AT or AAC Equipment:
Despite the major funding sources mentioned above, there are a number of
other smaller organizations that are possible funding sources. These include but are not limited to:
a. Disability Organizations that include groups
like Easter Seals, United Cerebral Palsy Association, the March
of Dimes, the Braille Institute, and Crippled Children's Services
(CCS).
b. Service Organizations: Included here are groups like United
Way, Lions Club, Masonic
Order, Elks Club, Rotary Club, Kiwanis Club and the Veterans
of Foreign Wars (VFW). In this
last case, the children of veterans may be eligible for receive assistance.
c. Private Organizations: Various companies in Private Industry,
Special Education Parent Organizations, Church groups and the PTA have also
provided funding for AT.
APPENDIX
A
Speech
Language Pathology Evaluation Report Form Examples
=============================================================
1 Example by Words +
Words+, Inc. 1
Speech
Evaluation Form
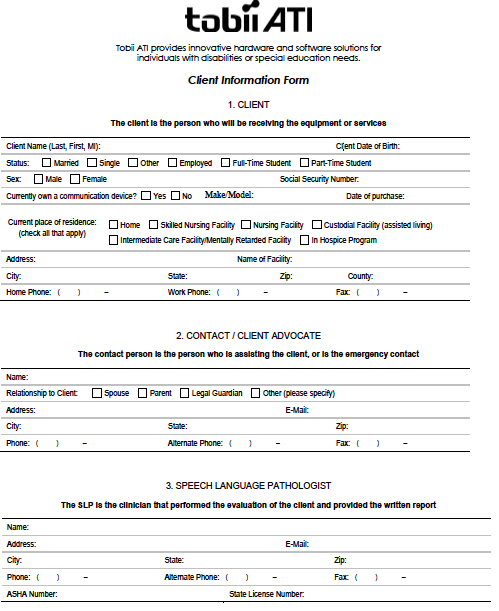
I. Demographic Information
Patient Name: Client
Advocate:
Address: Phone #:
DOB:
Medicare/Medicaid ID#:
Primary Diagnosis:
ICD-9: Onset:
Secondary Diagnosis:
ICD-9: Onset:
Speech Language
Pathologist Name: Phone #:
Address: Email
Address
Date of Evaluation:
Physician Name and
Address:
Phone #: Fax #
NPI# License #
II. Current
Communication Impairment
A. General Statement of
PatientÕs condition-diagnosis: List medications, if applicable
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
1. Type of Communication
impairment: Check all that applies
|
Dysarthria |
|
Aphasia |
|
Apraxia |
|
Aphonia |
2.
Severity of impairment: List impairment checked above with the
corresponding severity
|
Mild
|
|
Mild-Moderate
|
|
Moderate
|
|
Moderate-Severe
|
|
Severe
|
3.
Anticipated Course of Impairment: Check which applies No
|
detectible
Speech Disorder |
|
Obvious
Speech Disorder, intelligble |
|
Reduction
in speech intelligibly |
|
Natural
Speech supplemeted with SGD's |
|
No
useful Speech (SGD only) |
|
Loss
of Speech |
B. Comprehensive Assessment
1. Hearing Status
Does the patient possess the hearing ability to
effectively use a SGD
to communicate functionally? Yes ________ No________
Does the client use a hearing aid? Yes_______
No________
2. Vision Status
Does the patient possess the visual ability to
effectively use SGD to communicate effectively? Yes_______ No_______
Does the client wear prescribed eyeglasses?
Yes_______ No________
3. Physical
Status
Does
the patient possess the physical ability to effectively use a SGD and required
accessories to communicate? Yes _______ No _______
|
Comments
|
|
Motor
Skills |
|
Ambulatory
Status |
|
Direct
Selection |
|
Scanning
|
4. Language Skills
|
Linguistic
Impairment Severity: Check which applies Mild |
|
Mild-Moderate
|
|
Moderate
|
|
Moderate-Severe
|
|
Severe
|
Assessment
tools/tests used in evaluation:
|
Assessment
test |
|
Evaluation
|
Current
communication ability: Check which applies
|
Sign
Language |
|
Gestures
|
|
Pictures
|
|
Words
|
|
Writing/Spelling
|
|
Verbal
Speech |
5.
Cognitive
Ability
Impairment Level: Check which applies
|
No
Impairment |
|
Mild
Impairment |
|
Moderate
Impairment |
|
Significant
Impairment |
Abilities
with an SGD: Check which applies
|
Poor |
Fair
|
Good
|
Excellent
|
|
Memory
|
|||
|
Attention
|
|||
|
Problem
Solving Skills |
|||
Comments:___________________________________________
____________________________________________________
III.
Daily Communication Needs
1. Specific Communication Needs:
a. Client interacts daily with: Check all that applies
Family __________
Caretaker __________
Health Care Professionals __________
Community __________
b. Clients needs: Check which applies
Request Emergency Aid ___________
Obtain Medical Care ___________
Advocate for him/herself __________
Express pain/reaction to medication __________
Express hunger/thirst __________
Express likes/dislikes __________
Additional Needs: ___________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
2. Ability to meet communication needs with
Non-SGD treatment:
a. Speech Therapy
Date Began _____________ Date Ended:___________
Current Prognosis without a SGD: Check which applies
Poor ______
Fair ______
Good ______
Excellent
______
Future Prognosis without a SGD: Check which applies
Poor ______
Fair ______
Good ______
Excellent ______
b. Low Tech Strategies used during therapy sessions:
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
Results of Low Tech Strategies: Check which applies
Poor ______
Fair ______
Good ______
Excellent ______
Can the patients daily communication needs be met by
low tech AAC or no-tech AAC technique? Yes _______ No________
IV.
Functional Communication Goals: Level of communicative
independence the patient is expected to achieve outside the therapeutic
environment with an SGD.
Check all that apply:
_____ Client will independently communicate physical
needs and emotional status to immediate family/caretaker on daily basis, as
needed.
Expected length of time to achieve goal: Circle which applies
Immediate Short Term Long Term
_____ Client will describe her physical symptoms and
ask any questions when interacting with his/her physician and other health care
professionals.
Expected length of time to achieve goal: Circle which applies
Immediate Short Term Long Term
_____ Client will engage in social communication
exchanges with immediate family and extended members in person and by use of
the telephone.
Expected length of time to achieve goal: Circle which applies
Immediate
Short Term Long Term
_____ Client will
engage in social communication exchanges with friends at home and in other
community settings.
Expected length of
time to achieve goal: Circle
which applies
Immediate Short Term
Long Term
_____ Client will
engage in decision making of his/her own personal affairs.
Expected length of
time to achieve goal: Circle
which applies
Immediate Short Term
Long Term
V. Rationale for
Device Selection
A. General Features of
recommended SGD and accessories:
Input/output features
1. Direct Selection: Check
all that apply to client
_______Keyboard
access ability
_______Touch screen
_______Other, Please
Specify
___________________________________________
___________________________________________
2.Scanning:
A. Switch Access
Capability:
_____Single _____Double
_____Other, please specify
Comments:
_________________________________________
_________________________________________
_________________________________________
B. Method:
______ Linear ______
Row-Column ______Group
______ Other, Please
specify
Comments:
_________________________________________
_________________________________________
_________________________________________
C. Ques:
_______ Auditory
_______Visual
Comments:
_________________________________________
_________________________________________
_________________________________________
42505 10th St.
West, Lancaster, CA 93534 Tel: 1-800-869-8521 Fax: 661-723-2114 Words+,
Inc. 7
3.Symbols
_______Pictures
______Words/Phrases
_____Other, Please Specify
Comments:
_________________________________________
_________________________________________
_________________________________________
4. Other Features
a. Portability Access:
Check which applies
Carrying Case ________
Wheelchair Mounting:__________
(Please provide name and
manufacturer of wheelchair)
b. Battery time required-If
Medicare is a payer, please use ABN form
Long life ______
Additional Battery_____
c. Misc. Please list all that
are necessary-If Medicare is a payer please use
ABN form
Example: Environmental Control,
Additional RAM, additional switch, additional mount or mount pieces, larger
screen size, etc.
________________________________________________
________________________________________________
________________________________________________
B. Recommended Device
and Accessories
The clientÕs ability
to meet daily communication needs will benefit from an acquisition and use of
the HCPCS category:
______ E2500= Speech
Generating Device, digitized speech, suing pre- recorded messages, less than or
equal to 8 minutes recording time. Mini Message Mate
______E2502= Speech
generating Device, digitized speech, using pre- recorded messages, greater than
8 minutes but less than or equal to 20 minutes recording time. Message
MateÕs
______E2504= Speech
generating device, digitized speech, using pre- recorded messages greater than
20 minutes but less than or equal to 40 minutes recording time.
______
E2506=Speech Generating device, digitized speech, using pre- recorded messages,
greater than 40 minutes recording time.
______ E2508= Speech generating
device, synthesized speech requiring message formulation by spelling and access
by physical contact with the device. Say-it! SAM Communicator V2
_______E2510=Speech generating
device, synthesized speech, permitting multiple methods of message formulation
and multiple methods of device access. Freedom SGD, Say-it! Sam Tablet XP1
or SM1, Conversa, Freedom Lite Convertible,
Freedom Lite
_______Other please
describe:________________________________
_________________________________________________
C.
Trials with SGDÕs
Device #1
Name of Device:
Features:
Client Success: circle all that
apply
Poor Difficult Good Easy
Explain:
____________________________________________
____________________________________________
Device #2
Name of Device:
Features:
Client Success: circle all that
apply
Poor Difficult Good Easy
Explain:
____________________________________________
____________________________________________
Device #3
Name of Device:
Features:
Client Success: circle all that
apply
Poor Difficult Good Easy
Explain: ____________________________________________
____________________________________________
42505
10th ______ E2506=Speech Generating
device, digitized speech, using pre- recorded messages, greater than 40 minutes
recording time.
______ E2508= Speech generating
device, synthesized speech requiring message formulation by spelling and access
by physical contact with the device. Say-it! SAM Communicator V2
_______E2510=Speech generating
device, synthesized speech, permitting multiple methods of message formulation
and multiple methods of device access. Freedom SGD, Say-it! Sam Tablet XP1
or SM1, Conversa, Freedom Lite Convertible,
Freedom Lite
_______Other please
describe:________________________________
_________________________________________________
C.
Trials with SGDÕs
Device #1
Name of Device:
Features:
Client Success: circle all that
apply
Poor Difficult Good Easy
Explain:
____________________________________________
____________________________________________
Device #2
Name of Device:
Features:
Client Success: circle all that
apply
Poor Difficult Good Easy
Explain:
____________________________________________
____________________________________________
Device #3
Name of Device:
Features:
Client Success: circle all that
apply
Poor Difficult Good Easy
Explain:
____________________________________________
____________________________________________
D. Specific Recommended Device
A.
(Reference quote provided by Sales Representative, if applicable)
Name of Device:
Accessories:
Vendor:
E. Patient and Family Support of
SGD
Please identify if the client and
family members/caretakers are motivated and agree with the device selected.
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
F. Physician Involvement
A copy of this report was
forwarded to the clients treating physician and he/she will generate a prescription
for the recommended device and accessories.
VI. Treatment Plan
.
The client will
receive 4 hours of training with the local sales representative.
.
The client will
receive _______ therapy sessions with the Speech Language Pathologist once they
receive the device.
VII. Signatures/SLP Assurance
The Speech Language Pathologist
performing this evaluation is not an employee of and does not have a financial
relationship with the manufacturer/supplier of the device.
_____________________________________
SLP Name
Words+, Inc. 42505
10th St. West, Lancaster, CA 93534
Tel: 1-800-869-8521 Fax: 661-723-2114 10 j
ASHA #
State License
=============================================================
=============================================================
2 Example by Zygo:
|
Example 70 YEAR OLD WOMAN WITH
PROFOUND DYSARTHRIA SECONDARY TO ALS Facility Name MEDICARE FUNDING REQUEST |
|
I. DEMOGRAPHIC
INFORMATION
|
|
|
Patient's Name: |
Social Security #: |
|
Patient's Primary Contact Person: |
Relationship to Patient: |
|
Medical Diagnosis: Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis |
|
|
Date of Onset: |
|
|
Physician: |
Phone Number: |
II.
CURRENT COMMUNICATION IMPAIRMENT
A. General
Statements
Impairment
Type & Severity (ICD-9 Diagnostic Code: 784.5)
Secondary
to ALS, Mrs. _____ presents with a profound dysarthria and is functionally
nonspeaking. Produces differentiated vowels with varying intonation. Imitates
monosyllabic words, with referent known, with ____% intelligibility.
Oral motor
control limited to gross movements only, and these movements are imprecise,
reduced in range and executed slowly (e.g. open - close mouth, protrude
tongue). Patient receives nutrition through gastrostomy tube. Spontaneous
speech is limited to vocalizations.
Anticipated
Course of Impairment
Based on the Severe Dysarthria due to Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Staging
Scale (a 5-point scale, with 1 being no detectable speech disorder and 5 being
no useful speech), patient's speech is characteristic of Stage 5 - No useful
speech. Given the patient's current status and progressive nature of ALS, it is
anticipated that Mrs. ___'s condition will deteriorate further.
B.
Comprehensive Assessment
Hearing
No
problems with hearing noted or reported. Patient passes pure tone audiometric
screening for octave frequencies at 25 dB from 500- 4000 Hz. Attends to and
discriminates natural and synthetic speech at conversational loudness levels.
Husband may have slight hearing loss, although his hearing has yet to be
formally assessed. Husband successfully discriminated synthetic speech in SGD,
at sentence level, given occasional repetition (of spoken message) and reliance
on visual display. Patient and primary communication partner possess hearing
abilities to effectively use SGD to communicate functionally.
Vision
Patient
wears bifocal glasses at all times. Shows no problems with visual attention,
scanning, tracking, or acuity with glasses on. Discriminates ¼"
text on display positioned at midline, at a distance of approximately 18",
without difficulty. Possesses visual abilities to effectively use SGD to
communicate functionally.
Physical
The
patient is wheelchair dependent. Has an electric wheelchair (Jazzy 1100, with a
right joystick controller). Drives chair independently and safely. Seating
tolerance approximates 2 -3 hours. Patient referred to physical therapist for
recommendations to improve seating comfort and tolerance. Patient spends
several hours/day in a standard recliner chair. Needs access to SGD from both
wheelchair and recliner.
Patient
reports weakness in both upper extremities. Patient is right hand dominant.
Able to type on standard keyboard using middle right finger and left index
finger. Types quickly and with few errors. No indications of fatigue or
discomfort after typing several sentences. Does not require keyguard at this
point in time. Accommodations may be required as ALS progresses (e.g. keyguard,
scanning module/switch). Patient possesses the physical abilities to
effectively use a SGD with noted accessories to communicate functionally.
Language
Skills
Informal
assessment reveals oral and written language skills within functional limits.
Patient answers abstract yes/no questions with 100% accuracy and follows
multistage directions with 100% accuracy. Answers multiple choice questions
about a paragraph read silently with 100% accuracy. Types grammatically
correct, syntactically complex sentences. Formulates meaningful written
paragraphs independently.
Cognitive
Skills
Patient
retains task instructions without difficulty. Recalls 100% (5/5) of messages
stored under abbreviations. Identifies logical codes to abbreviate messages.
Spontaneously uses strategies to aid message production (e.g. abbreviates
words) Consistently gives partner feedback (using SGD and nonverbal cues) to
indicate if message is accurately interpreted. Corrects and clarifies messages
as appropriate. Spontaneously and appropriately shifts between communication
approaches to maximize communication efficiency. Demonstrates ability to use
word prompting and prediction. Possesses cognitive/linguistic abilities to
effectively use SGD to communicate and achieve functional goals.
III. DAILY
COMMUNICATION NEEDS
A.
Specific Daily Communication Needs
Primary
communication situations involve 1:1 and small group situations. Primary
environments are home and medical appointments. Primary communication partners
include husband, daughter, friends, paid caregivers, and medical staff.
Specific message needs include expressing needs, making requests, asking
questions, offering information, and expressing feelings/opinions. Patient
expresses strong desire to maintain her role as a decision maker in the home,
to socialize with friends and family, and to communicate directly with medical
staff regarding her disease and treatment.
B. Ability
to Meet Communication Needs with Non-SGD Treatment
Patient
has previously received speech maintenance therapy. However, given the current
severity of the patient's speech impairment, coupled with the progressive
nature of ALS, therapy to improve speech production is no longer indicated or
appropriate.
The
patient relies on yes/no responses, vocalizations, facial expressions, simple
gestures (e.g. pointing to items in environment), alphabet board and desk top
computer. Unaided approaches are effective for calling attention and indicating
very basic needs (e.g. pointing to
a cup to request drink).
The
alphabet board is used to generate novel messages during face-to-face
conversations with husband, daughter and a few close friends. The board is
adequate for basic needs that require a 2 or 3 word message; messages exceeding
2-3 words are difficult for partner to decode/retain. The board also requires
the partner to be standing beside the patient as she composes her message. This
can be tedious and time consuming for all partners and is not tolerated by
medical personnel. The board is ineffective in-group social situations, because
not all partners can see the board and follow along as the patient spells. The
board is not effective with hired caregivers because they cannot read English.
The desktop computer is used to prepare messages in advance for either the
husband or daughter. The computer is not portable nor does it have voice
output.
The
patient's current communication approaches do not permit her to convey the type
and complexity of information in the environments and with those partners with
whom she interacts on a daily (i.e. husband, daughter, care givers) or
intermittent basis (i.e. physicians, friends).
IV.
FUNCTIONAL COMMUNICATION GOALS
Upon
receipt of an SGD, therapy will target the following goals. Ms.___(Patient)
will:
- Demonstrate ability to master basic maintenance and operations of
SGD (on-off, adjusting menu features such as voice and display) with 100%
accuracy (within 2 weeks)
- Demonstrate ability to program stored messages independently with
100% accuracy (within 2 weeks)
- Convey basic needs/make requests to caregivers, by spelling or
retrieving pre-programmed message on SGD, independently and with 100%
accuracy (within 2 weeks).
- Initiate social greetings, offer information, ask questions,
express feelings and opinions through spelling and retrieving stored
messages on SGD, during 1:1 and group situations with familiar and
unfamiliar partners, independently and with 100% accuracy (within 3 weeks).
- Use strategies on SGD to expedite message production when sharing
information or asking questions of medical personnel, independently and
with 100% accuracy (within 3 weeks).
V.
RATIONALE FOR DEVICE SELECTION
A. General
Features of Recommended SGD and Accessories
Based on
the above noted comprehensive assessment, daily communication needs, and
functional communication goals, the patient requires SGD with the following
features:
Input/Message
Characteristic Features:
- Direct selection with index and middle fingers of both
hands/standard or mini keyboard (patient prefers QWERTY keyboard)
- Flexibility to accommodate changes in physical access (i.e.
alternative keyboard, scanning)
- Accessible from multiple positions (i.e. wheelchair, Lazy Boy)
- Alphabet based with multiple means of message formulation (i.e.
abbreviation expansion, word prediction, and pre-stored message recall)
Output:
- Text-to-speech speech synthesis (given that patient has novel
message needs and is relying on spelling as primary means to generate
messages)
- Two-way visual display to aid husband (who has suspected hearing
loss) to interpret messages
- Capability to facilitate communication at a distance.
Other
features:
- Portable to accommodate conversational needs in various locations
within home and at medical appointments
- Long lasting battery to ensure device is operational in various
locations and to minimize need to be close to electrical outlet.
B.
Recommended Medicare Device Category and Accessories Codes
The
individual's ability to meet daily communication needs will benefit from
acquisition and use of the SGD Category E2510 and equipment that enable device
to be mounted from SGD accessory code (E2512).
C. Trials
with SGDs
Patient
participated in trials with 3 SGDs in Category E2510 that have the input and
output features similar to those delineated above. The SGDs included
Spok21-Combi, the Allora, and the Polyana 4 with Persona. Both current and
future communication needs were considered as her physical condition is likely to
deteriorate.
- Spok21. Patient had difficulty with remembering where stored
messages were put.
- Allora. After demonstration only used the Allora to generate novel
messages. Used all function keys without difficulty. Given the scanning
limitations, the inability to see the target during the complete scan
cycle, and the small visual display the Allora is not an optimal solution.
- Polyana 4 with Persona. The patient independently utilized the
Polyana to communicate her needs. Spelled lengthy, complex messages
without difficulty. Used word completion and word prediction with 100%
accuracy and recalled all messages stored under abbreviation/expansion.
The husband successfully interpreted all of the patient's messages relying
on speech output and only once had to look at the visual display. The patient was shown scanning
features and was able to select messages using row-column scanning.
D.
Recommended SGD and Accessories
Based on
comprehensive assessment and SGD trials, it is recommended that the patient be
fitted with the Polyana 4 with Persona and wheelchair mount to secure the
device and allow independent access. The recommended wheelchair mount is
designed to accommodate the Polyana 4 and will enable her to use the device
throughout most of the day.
|
Part Number |
Description |
|
Polyana 4 with Persona |
Polyana 4 with Persona
text-to-speech communication device |
|
039-9089-55 MS-48 |
Medium weight mount,
3x1" chair clamp, 1x2Õ tube, pin release, quick release tray |
|
CM-40 |
Lolly Switch |
Polyana
and accessories are available from:
ZYGO
Industries, Inc. 800 234-6006 or 503 684-6006 FAX 503 684-6011
P.O. Box 1008
Portland, OR 97207-1008
E. Patient
and Family Support of SGD
The
patient and her husband demonstrate motivation to maintain SGD. Have
established basic skills with the Polyana. The patient understood the pros/cons
of different devices and identified the Polyana as the optimal device for her
needs.
F.
Physician Involvement Statement
A copy of
this report has been forwarded to the patient's treating physician (DR. É #XXX)
on ______ (date) for review and prescription.
VI.
TREATMENT PLAN
Upon
receipt of SGD, it is recommend that the patient receive 45 minutes of
individual therapy and one hour of group therapy weekly for 8 weeks (total 16
sessions). These sessions will address goals listed in Section IV of this
report. An additional two hours of training are recommended to train caregivers
to program the device.
V.
SIGNATURES / SLP ASSURANCE OF FINANCIAL INDEPENDENCE
The
Speech-Language Pathologist performing this evaluation is not an employee of
and does not have a financial relationship with the supplier of the SGD.
____________________
XXX MS CCC-S
Speech Language Pathologist
ASHA #
State Lic.
GLOSSARY OF TERMS
Allowable
The amount of
money for which your insurance company will allow a claim to be processed. The
client's co-insurance is usually based on their allowable amount. For example,
if the allowable amount is $5,000.00, and the client's co-pay is 10%, the
amount the client will owe is $500.00.
Assignment of Benefits (AOB)
Form
signed by the policy holder that allows the insurance company to pay ZYGO
Industries, Inc. or its dealers directly. Without an AOB, the policy holder may
receive the insurance payment.
Certificate of Medical Necessity (CMN)
This
is usually a state-specific form which is signed by the physician or speech
therapist.
Claim
Billing submitted
to the insurance company after the equipment has been delivered.
Client Advocate
Person
who is representing the client during the funding process. This person is usually
a speech therapist or case manager.
CPT Code
The Current
Procedural Terminology code describes the type of services that are being
supplied. This is generally the same as a HCPC Code.
Custodial Care Facility
Facility
that provides room, board, and assistance with daily living activities, such as
feeding and dressing. This care is generally on a long term basis and does not
entail the continuing attention of trained medical personnel.
Deductible
That
amount that the client must pay annually before benefits will be paid by the
insurance company.
Durable Medical Equipment (DME)
Systems
made to withstand repeated use that are used for the treatment of an injury or
disease. Speech Generating Devices have been classified as Durable Medical
Equipment.
Explanation of Benefits (EOB)
The
statement from the insurance company showing the services and amounts that were
paid by the policy. This is also known as a remittance.
Exclusions
Services
for which the insurance company will not pay.
Funding Questionnaire (FQ)
A
questionnaire that is usually completed by a family member or other contact
person which includes important information such as the client's address,
physician, insurance information, and a list of the equipment that they wish to
order.
HCPC
Code that is used
to describe the services rendered. For example, the Polyana with Persona has a
Medicare HCPC code of E2510.
Hospice
Supportive care
given to a terminally ill client and their family. The focus of this care is to
enable the client to remain in the familiar surrounding of their home for as
long as they can. Hospice care may be either inpatient or outpatient.
ICD-9 Code
International
Classification of Diseases. Insurance code that describes a client's medical
condition or diagnosis.
Insurance Letter of Requirement (ILR)
This
letter is sent to your insurance company by your funding coordinator and
explains the details that should be included in a private insurance
authorization. An approval form is also included with this letter. Insurance
companies may complete the approval form instead of creating a letter.
Invoice
Itemized
statement explaining what items or services have been delivered.
Letter of Medical Necessity (LMN)
A
letter explaining the medical need for AAC services. This letter can be written
by a physician, speech therapist, or occupational therapist. These letters
usually give the client's diagnosis and a brief explanation of why services are
necessary.
Maximum Out of Pocket
The
maximum amount a client will pay towards their deductible and co-insurance
during the year.
Managed Care Organization (MCO)
Any
insurance plan in which the client will need to have services approved by their
plan's referring physician or medical group.
Medicaid
State-sponsored
medical plan. Eligibility for these plans is traditionally based on a family's
income. May also be called Title 19.
Medicare
Federally-sponsored
medical plan. Clients become eligible for this program when they turn age 65 or
have a qualifying disability. There are two separate programs under
Medicare
Part A (hospitalization) and Part B (medical). Clients must pay
a monthly fee for Part B coverage. speech generating devices are covered under
Medicare Part B.
Medicare Supplement
An
insurance policy that covers Medicare co-payments and other services. This
policy must be purchased by the Medicare beneficiary.
Non-Participating Provider
Provider
that has not contracted with a health insurance company to provide services at
a reduced fee. Also referred to as an Out of Network Provider.
Original Documentation
Prescription
and speech evaluation that has an original signature. The signature page on the
evaluation and the doctor's prescription cannot be stamped, copied, or faxed.
Medicare requires that original documentation be on file with the vendor for
any product.
Payment Agreement (PA)
Form
signed by a policy holder stating that they agree to cover any amounts not paid
by the insurance company.
Place of Service (POS)
The
location where the medical services will be provided or used. It is important
that we know whether a client lives at home, in a group home, or in a nursing
facility. Some funding sources will not cover clients that live in a nursing
facility.
Pre-certification
See
Prior Authorization.
Pre-determination
A
review done by an insurance company to determine whether a service will be
considered a covered benefit.
Prior Authorization
Approval
issued by the insurance company before equipment is delivered. Authorizations
are normally issued by nurse reviewers at the insurance company who review the
doctor's orders and other documentation to ensure that a service is medically
necessary.
Referral
Specific
directions or instructions from a client's primary care physician. Referrals
may be on paper or electronic and are usually required by HMO policies.
Release of Information (ROI)
A
form that is signed by a client or their guardian and gives permission for the
vendor to release medical documentation to insurance companies and other
funding sources.
Remittance
A
statement sent to medical providers from the insurance company to show the
payment that was issued. Also called Explanation of Benefits (EOB).
Rx
Prescription.
This must be signed by a medical doctor or dentist.
Sole Source Supplier
A
provider who is the only source for a particular service or type of equipment.
Subscriber
The
employee covered under an employer's group insurance policy. Also referred to
as the policy holder.
Skilled Nursing Facility (SNF)
A
facility which provides inpatient skilled nursing care and related services to
patients who require medical, nursing, or rehabilitative services but do not
require the level of care provided in a hospital. If a person is in this type
of facility, they are not able to use Medicare as a funding source.
Stop Loss
See Maximum Out
of Pocket.
UPIN
Unique Physician
Identification Number. Identification number that is used to identify the
physician who signed the prescription. This number is used when filing claims
to insurance companies.
Usual and Customary
Charges
Also referred to as Reasonable and
Customary Charges. An amount determined by an insurance company that represents
a routine charge for a medical service by similar medical and professional
providers in the same geographical area. Allowable amounts are normally based
on the Usual and Customary Charges.
========================================================================
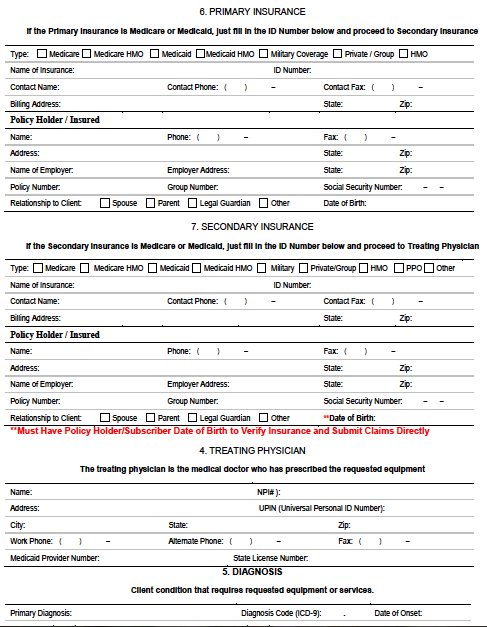
EXAMPLE 3 EVALUATION BY PRC
AAC Evaluation for John
Doe
Submission Type: Purchase
Date of Evaluation
5/30/2008
Date of Report 7/16/2008
Client Information
Name: John Doe Telephone:
(330) 111-2222
Address: 123 Main St, N/A
Wooster, OH 44691 Place
of Residence: Home
Medicaid ID Num.:
111111111 Date of Birth:
1/1/1998 Age: 10
Medicare ID Num.: N/A
Medical Diagnosis: Cerebral Palsy (343.9)
Insurance Policy Num.:
XYX0000000000222 Onset: 1/1/1998
Referred By: James Smith
Speech Diagnosis: Aphasia (784.3)
Licensed SLP: Mary Bing
Onset: N/A
Description of Impairment
Impairment Type, Severity
John is a 10 year old male diagnosed with Cerebral
Palsy (343.9).
Briefly describe diagnostic assessment,
results of formal and informal tests, speech intelligibility.
John is highly motivated to communication with a
speech generating device. He recalls symbols locations, device operations and
instructions.
He initiates communication spontaneously with his
family, physician, nurses, and myself. He is able to spell.
Briefly describe current communication system
and explain why it does/does not meet the client's current needs.
John currently uses a Pathfinder. The Pathfinder has
older technology. It features a static display with 128 locations. John's
vision has changed
and the icons are too small for him. Also, he has
some lost motor control in his right arm and will need a more comprehensive
access method.
Due to this loss of motor control, sign language is
not an option.
/ X / Given the severity of the communication
impairment as described above the Client's speech does not meet his/her daily
communication needs.
/ X / Speech intelligibility in spontaneous
communication is judged to be 95% unintelligible to the unfamiliar listener.
Anticipated Course of Impairment
The Client's condition is
chronic and stable and independent communication is expected to remain stable
at the present level. Therefore it is anticipated that the Client's natural
speech will not be sufficient to meet daily communication needs for the
client's lifespan. The prognosis for
speech production to meet
communication needs is poor.
Hearing Status
History of hearing
impairment: / / A history
/X / No history
Client has: No other
hearing issues
If the Client has a
hearing loss, please specify the percentage: %
Modification to SGD
With the modification
indicated below, the Client demonstrates adequate hearing ability to use a SGD
to communicate functionally.
/X /
No modifications needed
/ / Specify Speech: Synthesized
/ / Specific speech output options: (describe type of speech
synthesizer, voice, digitized, loudness):
John presents with no history of a
hearing impairment, so volume is not an issue.
/ / Additional Comments:
N/A
Visual Status
The Client has a history of mild uncorrected visual
impairment. Informal observation of functional visual performance during the
SGD assessment
revealed the Client required the modifications
listed below to use a SGD effectively given current vision status.
Modification to SGD
/X /
No modifications needed
/ / Client will respond to: Dynamic display
/ / Font size used on SGD display and/or symbol labels should
be: Medium
/ / Picture-symbols and/or icons should be the following size
(inches): .75 x .75
/ X / A flat display is required to reduce
visual tracking requirements (e.g., need to alternate focus between keyboard
and display to monitor
selections)
/ / If applicable, color contrasts are needed to enhance
visibility of text or symbol on SGD.
/ / Number of items per display should be: 84
/ / Ability to hide keys is required to reduce visual distractibility.
/ / Auditory prompts from device are needed to assist in message
preparation/selection.
/ / Additional Comments: N/A
Physical Abilities
Physical Status
The Client was able to
successfully access SGDs presented at the evaluation with the following
selection technique/modifications.
Direct Selection: Infrared Headpointer (Tracker, Headmouse)
Type: N/A
Additional Info: N/A
Scanning: N/A
Type: N/A, N/A
Additional Info: N/A
Requires multiple access methods? No
If Yes, Please
describe: N/A
Briefly describe Clients ability to use the access
method and any modifications needed for success.
(keyguard, finger splint,
stylus, switch mount, switch location)
John is unable to access a device through direct
selection due to loss of motor control in his right side. There has been no
control in his left side
since birth. He will need a head pointing option
such as a embedded Tracker.
Mobility
Client is: / / Ambulatory /
X/ Non-ambulatory
Assist used for mobility:
Power wheelchair
For individuals using
wheelchairs:
Wheelchair Mounting
System: Will not be required
If a mounting system is
required, please specify make/model of wheelchair:
Make: N/A
Model: N/A
With the above modifications/considerations, the
Client possesses the physical abilities to effectively use a SGD and required
accessories to
communicate.
Client will transport the SGD by: Wheelchair Mount
In pounds, the weight of SGD must be no more than: 6
lbs.
The physical size must not exceed (H x W x D):
Vanguard Plus is 13– x 10– x 3–
Carrying case is required
for transporting: /
/ Yes /
X / No
Additional comments:
John will be able to use his wheelchair mount from
his current Pathfinder to transport his new device.
Language Skills/Ability
Speech and Language
Abilities Determined by: (check all that apply)
/ / Report by family, teachers, caretaker
/ / Informal assessment
/ / Observation
/ / Trial therapy
/ / Formal testing
Formal tests
administered:
Approximates single word
spelling at the 4th grade level.
The Client presents with
moderate impairment in language functioning as it relates to using an
appropriate SGD. The Client possesses the following
skills/abilities:
Receptive Language
/ / Attends when spoken to
/ / Appears to recognize name
/ / Understands references to items that are out of sight
/ / Understands frequently used words
/ / Understand one or two part directions
/ / Understands simple questions
/ / Understands virtually everything that is said to Client
It is difficult to
determine what is understood due to Client's motor handicap, but individuals
familiar with Client report he/she understands most that is said to him/her.
Additional receptive
language information:
N/A
Expressive Language
Communicates expressively
using: (check all that apply)
/X /
Pointing
/ / Signing N/A
/ / Eye gaze
/ /
Vocalizes/approximates words N/A
/ / Uses single pictures/symbol to convey a
message
/ X / Uses multiple pictures/symbols to
convey a message
/ X / Uses single word to convey a message
N/A
/ / Uses
words to convey message N/A
/ / Uses
spelling to convey a message
/ / Uses word
prediction to convey a message
/ / Can use
all three methods of organizing vocabulary; Single-meaning
pictures, Multiple-meaning pictures,
spelling/word prediction.
Additional expressive
language information:
N/A
When Client's receptive and expressive language
skills are compared, Client appears to understand significantly more than
he/she is able to
communicate, indicating the need to focus on
expanding his/her ability to communicate.
Pragmatics
/ / Uses language for different purposes Feelings, Requesting,
Protesting
/ / Changes language according to the listener or situation
/ / Gives background information to an unfamiliar listener
/ / Speaks differently in the classroom than during recess
Follows rules for
conversation: Stays on topic, Uses facial expressions and eye contact.
Although Client uses
non-symbolic strategies such as facial expression for a few of the different
purpose of communication, he/she is unable to
communicate this
information using language.
Reading
Functional reading is:
Paragraphs
Additional reading
comprehension information:
N/A
Writing
/ / Unable to produce written language
/ / Produces written language by: Typing
/ / Produces written communication using: Words
(independent),
Sentences
SGD must use this method for message production: A
combination of spelling, words and pictures
Nature of the message the client was able to
generate: Phrase
How much instruction did
the client require to produce messages: Minimal
Describe the cueing needed for message generation: No assistance or cueing.
Provide additional
details as needed to support the Client's potential use of an SGD for
functional communication in ADL's:
N/A
The Client's linguistic
performance with the SGDs presented during the evaluation indicated the
necessary language skills to communicate using a
SGD.
Cognitive Abilities
Level of impairment in
cognitive functioning: Mild
Length of assessment
and/or training trials: One month

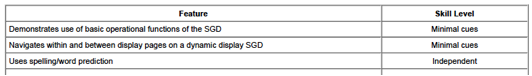
The Client demonstrates
the necessary cognitive abilities (i.e., attention, memory, and problem-solving
skills) to learn to use a SGD to achieve
functional communication
goals.
Provide additional
details as needed to support the Clients cognitive ability to use or learn to
use an SGD for functional communication in ADL's:
John currently uses a speech generating device,
Pathfinder. He is fully capable and has the cognitive ability to use such a
device. His cognition
falls within functional limits. He was able to
retain instructions without difficulty. He was able to create phrases using
icons as well as spelling
methods.
Daily Communication Needs
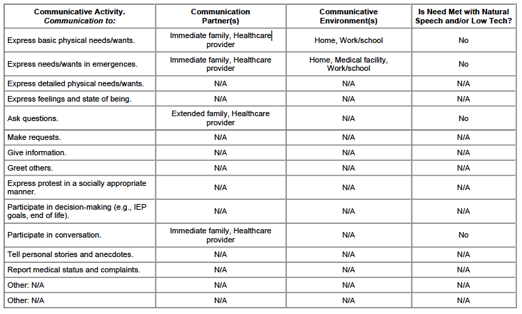
Ability to Meet
Communication Needs With Non-SGD Treatment Approaches
Speech therapy to
improve/increase functional speech is not a viable option to meet the Client's
communication needs because:
/ / The Client has a degenerative condition for which speech
therapy to improve/increase functional speech production is not effective.
/ / The Client received speech therapy for n/a with no
significant increase/improvement in functional speech production.
/ / The client's speech functioning has been static for n/a and
no improvement is expected.
Briefly explain why
natural speech and/or low tech communication methods are not effective. For
example, caregivers do not know sign language, need to get attention from a
distance, talk on the telephone.
Johns is unable to sign due to his motor control.
The results of the
communication needs assessment as documented in the previous section indicate
the majority of Client's daily functional
communication needs
cannot be met with natural speech and/or low tech communication devices.
Therefore the Client requires a SGD to achieve
and/or maintain
functional communication ability in activities of daily living.
Functional Communication
Goals
The Client's immediate,
short term and long term goals and estimated times to completion following
receipt of the recommended SGD are
Functional Communication
Goals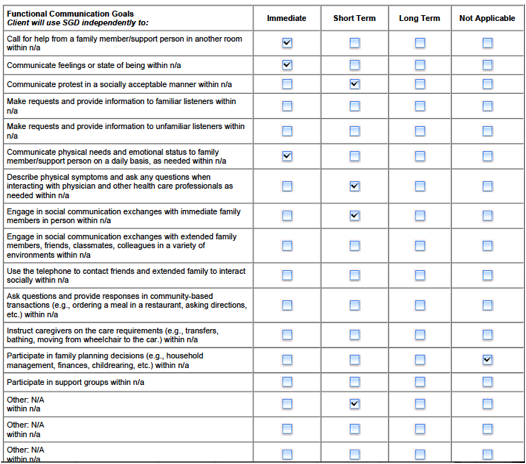
Input & Output Features
Input Features![]()

Output Features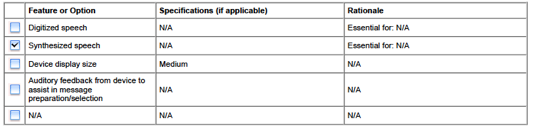
Language Characteristics
and Device Features
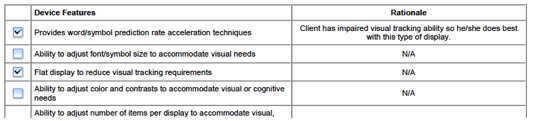
![]()
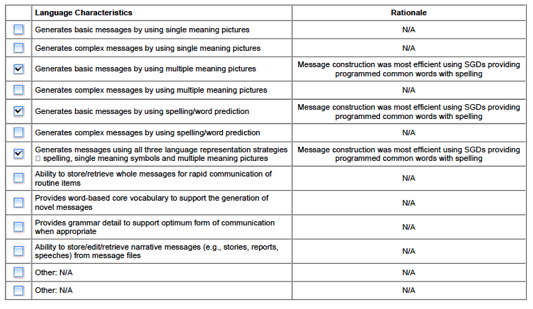
Other Features or Options
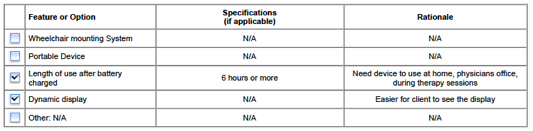
Equipment Evaluated and Device Code
Recommended Speech Generating Device Code
Based on the Client's communication needs and
considering the Client's visual, hearing, physical, language and cognitive
status as well as
specified features described in this report, SGD's
in this Medicare/CPT code category are recommended: E2510 (synthesized, multi
access, multi
message)
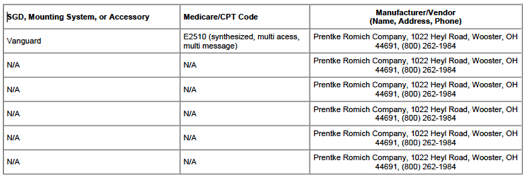
Speech Generating Devices and Accessories
Evaluated
You must consider 3 or
more SGD–s for the client. List
the SGDs and accessories that were considered during the assessment. Include
the product name and the manufacturer for each SGD:
ECO 14 with integrated headpointing Vanguard with
integrated headpointing Vantage with integrated headpointing (all of the above
devices are manufactured by Prentke Romich Company)
SGD Evaluation
Procedures used for evaluating the SGD's
When assessing the
Clients ability to use the selected SGDs the following procedures were used:
The ECO, Vanguard, and Vantage were presented to the
John. These devices we used because they all feature Unity, which the client is
familiar
with due to him using the Pathfinder. Since he was
familiar with the Vanguard, John was able to produce sentences and phrases with
all three
devices. John did have trouble viewing the smaller
icons (144 locations) on the ECO. He found that Vantage also too small. He was
most
efficient on the Vanguard. He was able to
successfully access the device with the embedded Tracker. He was not able to
access any of the
above devices with direct selection even with a
keyguard present.
Outcome of the SGD evaluation
For the following reasons
the Vanguard device was selected as the most appropriate SGD for the
Client. Briefly explain why the
selected SGD is the best fit based on client needs (specifications) and SGD features:
The Vanguard was the easiest for John to view. The
device will be mounted on his power chair with his current mount, so weight is
not a factory.
John is familiar with Unity, so he will not have to –relearn–
language. He was able to successfully one, two, three word phrases, and spell.
The other SGDs evaluated
were ruled out for the following reasons:
Size was too large or too small
Speech Generating Device and Accessories
Recommended
The individual's ability to achieve functional
communication goals requires the acquisition and use of the SGD,
mounting/carrying devices and
accessories listed below. This SGD represents the
clinically most appropriate device for John Doe.
Please specify the
product details for the order. For example: the color of the SGD and/or the
size of the keyguard. Part numbers and product
options are available in
our catalog or in our e-Store. Please click the Store link at the top of the
page for the current product offerings.
If a wheelchair mount is
being requested, please view our E-Store or current catalog for the type of
mount and the specifications of the mount. For example, bar length and tubing
size should be selected. This information is needed prior to the submission of
a request to the third party payer(s).
Support, Treatment Plan
and Signature
Client/Family
Support of Speech Generating Device
Please indicate the
Client's family or support person(s) present at the evaluation who are
supportive of the necessity of the SGD for meeting the
Client's communication
needs: Immediate family
Physician
Involvement Statement
This report was forwarded
to the treating physician, James Smith, ; (330) 222-3333, on 7/16/2008.
The physician was asked to write a
prescription for the
recommended SGD and accessories.
Treatment
Plan
The client's treatment
goals would best be met in this type of setting:
A combination of group and individual treatment
SLP
Assurance of Financial Independence and Signature
The Speech-Language
Pathologist performing this evaluation is not an employee of and does not have
a financial relationship with the supplier of any SGD.
====================================================
EXAMPLE 4 BY DYNAVOX:
FOR
SAMPLE USE ONLY – Please retain for your records
Evaluation
Report Structure for Funding of
Speech
Generating Devices
Request for Speech
Generating Device (SGD) Funding:
Section 1:
Demographic Information
á Patient: full name,
complete address & telephone number
á Date of Birth
á Medical Diagnosis (do not
list code)
á Communication Diagnosis
(do not list code)
á Date of onset
á
Medicaid/Medicare/Insurance Number(s)
á Primary Contact: complete
address, telephone number & relationship to
patient
á Physician: full name,
complete address & telephone number
á SLP: full name, complete
address & telephone number
á Date of SLP evaluation,
date of report
Section 2: Current
Communication Impairment
A. General Statements
1. Impairment type and
severity
Indicate type of
communication impairment
á Describe impairment severity
This section should
explicitly demonstrate how the medical condition results in
severe expressive speech
impairment.
2. Anticipated Course of
Impairment
á This section should
demonstrate the current status and the expected
course of the speech
impairment as it relates to the underlying
disease/condition.
á Indicate the expected
course of impairment for conditions that are
stable as well as those
that are progressive
á EXAMPLES: "The
patient has severe dysarthria due to cerebral palsy.
The condition is stable and
speech intelligibility is not expected to
improve;" or "The
patient has severe dysarthria due to amyotrophic
lateral sclerosis.
Currently speech rate is ## (half of normal),
indicating an expected
precipitous decline in intelligibility. Speech
intelligibility will
continue to deteriorate. This patient will require use of
an SGD throughout the
course of this disease."
Rev. 1/2009
B. Comprehensive Assessment
1. Hearing Status
á Describe the
communicator's hearing relative to communicating
with a SGD (along a
continuum from normal hearing to deafness).
á Include communication
partner's status, if relevant.
á Include specifics (if
related to SGD use/selection) regarding acuity,
localization, understanding
of natural speech, understanding
speech generated by an SGD.
á The report should
state: "The patient possesses the hearing
abilities to effectively
use an SGD to communicate functionally."
2. Vision Status
á Describe the
communicator's vision relative to using an SGD (along
a continuum from normal vision
to blindness).
á Include the following
elements if/when pertinent to SGD
use/selection: acuity,
visual tracking, visual field, lighting needs,
angle of view, size of
symbols, contrast (color, detail), and spacing.
á The report should
state: "The patient possesses the visual
abilities to effectively
use an SGD to communicate functionally.Ó
3. Physical Status
á Describe pertinent
considerations regarding motor skills,
ambulatory status,
positioning and seating.
á Describe how the person
will access the SGD (direct selection,
scanning) and the person's
access requirements.
á Describe if
accommodations may be required over time to deal with
changes in physical access.
Keep in mind, however; that Medicare
will not cover items that
are needed for future rather than current
medical necessity.
á The report should
state: "The patient possesses the physical
abilities to effectively
use an SGD and required accessories to
communicate."
á This is the area of the
report where recommendations for
accessories (keyguard,
switch, mount, etc..) are indicated.
4. Language Skills
á Describe the level of
linguistic impairment (no impairment to severe
language impairment) as it
relates to the person's ability to use an
SGD.
á Consider describing:
o performance on any language
assessments completed
o competency of ability to
develop functional language skills
Rev. 1/2009
o type and level of symbol
use by the individual. Does person
require pictographic
symbols, words, letters, and/or a
combination of symbols?
o linguistic capacity to
formulate language/messages
o level of independence in
formulating messages using
language
5. Cognitive Skills
á Describe the level of
cognitive impairment (no impairment to
significant cognitive
impairment) as it relates to the person's need
for and ability to use an
SGD.
á Describe the person's
attention, memory, and problem-solving skills
as they relate to using an
SGD to enhance or develop daily,
functional communication
skills.
á The report should
state: ÒThe patient possesses the
cognitive/linguistic
abilities to effectively use an SGD to
communicate and achieve
functional communication goals.Ó
á EXAMPLE: Mr.
Smith's attention, memory and nonverbal problemsolving
skills are within
functional limits. He sustained attention for
a two-hour evaluation,
recalled how to turn on and off an SGD
(after initial
instruction), and independently navigated between two
pages on an SGD. He has the
attention, memory and problemsolving
skills to use an SGD to
achieve his functional
communication goals."
Section 3: Daily
Communication Needs
A. Specific Daily Functional Communication Needs
á This section should list
the person's daily functional communication needs in areas described:
o Communication to enable
person to get physical needs met (e.g.,
ability to communicate in
emergency situations, directing behavior
of caregivers, advocating
for him/herself, communicating with
family, friends, medical
professionals or clergy using the phone)
o Communication to enable
person to obtain necessary medical care
and participate in medical
decision-making, (e.g., reporting medical
status and complaints,
asking questions of medical providers,
responding to medical
provider's questions, discussing choices for
end of life care,
communicating with medical providers by phone).
o Communication to enable
person to carry out family and
community interactions.
Rev. 1/2009
B. Ability to Meet
Communication Needs with Non-SGD Treatment Approaches
áThis section should
document why the patient is unable to fulfill daily
functional communication
needs using natural speech (or speech aids)
and non-SGD treatment
approaches.
o
Discuss success of speech therapy (to date and future prognosis) without an SGD
o
Discuss the individual's ability to use low-tech strategies and natural modes
of communication to met daily functional communication needs.
o
Discuss why an SGD is required in addition to, or instead of low tech strategies
and natural speech.
o
Show explicitly that other forms of treatment have been considered and ruled
out.
o
Mention issues related to communicating with primary partners and caregivers in
specific contexts.
á The report should
state: "The patient's daily functional communication needs cannot be
met using natural communication methods or lowtech/ no-tech AAC techniques because
of ______________________ (be specific).
Section 4:
Functional Communication Goals
Documented goals MUST be a
part of the justification report.
á Document 2-3 goals in
each time frame, short (2-3 mo), intermediate (6 mo.) and long term (1+ yr.) to
be achieved after the device has been delivered.
á Goals should correspond
to specific daily functional communication needs
(including specific
contexts and communication partners as well as
communication functions)
and illustrate how the patient will benefit from the acquisition of and
training on the SGD.
EXAMPLES:
Adult oriented
o 1) Mr. ___ will be
able to independently communicate physical needs and emotional status to his
wife on a daily basis, as needed within 2 months.
Rev. 1/2009
o 2) Ms. ___ will describe
her physical symptoms and ask any questions when interacting with her physician
and other health care professionals as needed within 6 months.
o 3) Mrs. ___ will
engage in social communication exchanges with immediate family and extended
members in person and by use of the telephone within 1 year.
Child oriented
1) ___________will
answer (wh) questions by sequencing a minimum of 3 pictures/words from at least
2 category pages on his
communication device
(master page, action words, things and/or describing words) ) to express a
novel and grammatically correct thought ( eg. I like bubbles), within 6 months.
2) Using the QWERTY
keyboard on his communication device ________________ will independently spell
out simple novel answers to questions using word prediction, editing keys and speak
keys as needed 80% independently, within 1 year.
Section 5: Rationale
for Device Selection
This section will explain
why certain device features are required. The rationale will relate the
person's skills and abilities as described in Section 2.
This section provides data
that leads first to the selection of a specific device code and second to a
specific device within that code, as well as specific accessories.
In order to make these
decisions, SLP's may work with OT's, PT's, Rehab Engineers, and use AAC
devices, computer or manual simulations to gather
pertinent data.
The report should state: "This individual requires a speech generating device with
(list specific features) to meet the person's functional communication
goals."
A. General Features of
Recommended SGD and Accessories
1. Input
Features/Selection Technique
A. Direct Selection
á
Keyboard/Display: dynamic/static, number of keys/locations
á
Activation Type: touch sensitive, pressure sensitive, adjustable
á
Optical pointer, head mouse, eye gaze, other (specify)
B. Scanning
á
Display: number of keys, dynamic/static
á
Mode: visual, auditory
Rev. 1/2009
á
Type of scan: linear, row/column, group/row/column, directed
(joystick,
trackball), adjustable speed
á
Switch: type (pressure, feedback), position, mount
C. Encoding Type
á
Position, category, semantic compaction, numeric, alphabetic, Morse code, other
(specify)
2. Message
Characteristics/Features
A. Type of Symbols
á Tactile, pictures
(note quality, color vs. black & white), symbols (commercially available,
individualized), words, phrases, letters
B. Storage Capacity
á Message length
needed
á Number of
different messages being stored or formulated
á Other (specify)
C. Vocabulary
Expansion and Rate Enhancement
á Screens or levels
á Word prediction
á Other (specify)
3. Output Features
á Voice Output
á Visual Display
á Feedback
4. Other Features (NOTE:
These relate to AAC accessories)
á Portability
á Size and weight,
transport/mount, case/carrier requirements
á Battery time
required
á Other
5. Description of
Equipment Used and/or Considered During the Evaluation
á Include evidence
that the individual was present and actively
participated in the
assessment process. Discuss assessment outcomes that demonstrate the person's
ability to use the SGD and recommended accessories.
á Discuss other
SGDÕs considered and why they were not
appropriate for this
user (for example if
recommending a
device in the E2510
codes you must rule out another device in codes E2508 and E2506). You do not have to try each device considered with the user
if it can be ruled out without a trial.
á Please include low
tech as well as high tech devices.
6. SGD and Accessories Recommended
á
List the specific SGD and accessories and include medical
justification as to why this SGD and specifically the accessories
being requested will
enable the patient to achieve functional
communication goals,
as stated earlier in the report.
The report MUST
state, "The individual's ability to achieve his/her functional
communication goals requires the acquisition and use of the (name the device)
and (name the specific accessories). This SGD (and these accessories)
represents the clinically most
appropriate device
(equipment) for (name of client)."
"Using my clinical
expertise, I have determined that the XYZ device (and accessories) is (are) the
most appropriate means of communication for John Doe.
(If trial was
completed or required, please make sure to mention that, ÒJohn has had an
adequate trial with the XYZ device or similar device, therefore I am
recommending a purchase of this device (equipment) for John.Ó)
Recommended
Equipment
___________________________________________
___________________________________________
___________________________________________
___________________________________________
___________________________________________
EXAMPLES:
E2510 Series 5 V
E2512 Wheelchair Mounting
System – to position the SGD in the
optimal place for effective
visual and physical access of the device.
OR
Switch Mount – this
mount is necessary to position the switch in
the proper place for
optimal use.
E2599 User Accessible Carry
Case – for protection of the device while be used throughout the day and
during transport.
OR
Keyguard – this
plastic piece with holes cut in it to coordinate with
the communication squares
on the SGD, will provide support and
guidance for direct access
of the desired square and will help
alleviate Òmiss hitsÓ.
OR
EyeMax - The patient is
experiencing weakness of the upper and
lower extremities, his
respiratory musculature, laryngeal
musculature and oral/facial
musculature. He is able only to
consistently move his
eyeballs laterally and vertically, to indicate
yes and no responses to his
caregivers. This leaves him virtually
Òlocked inÓ his own body.
Eye gaze is the only functional
movement this patient can
achieve, therefore and eye gaze system
is the only method of
access available.
Headmouse or Tracker Pro
– this is an alternate access device
where the user will move
their head to control a pointer on the
screen. This pointer will
activate the desired square when the user
dwells on it.
7. Patient and Family Support of SGD
á Discuss
participation of the family/caregiver/advocate and state that they agree to the
selected SGD (and accessories) and will support the equipment and its use for
daily communication.
8. Physician Involvement Statement
á The report should state:
"This report was
forwarded to the treating physician
Name
________________________________________
Address
______________________________________
City, State, Zip
_________________________________
Telephone #
__________________________
on _______(date), so that
he/she can write a prescription for the
recommended SGD and
accessories."
á NOTE: The date that the
SLP forwards the SGD device assessment report should be BEFORE the date on the
doctor's prescription.
Section 6: Treatment
Plan
Address all functional
communication goals previously stated for the beneficiary and identify the plan
for achieving these goals using the SGD and accessories.
á
Frequency of SLP treatment
á
Schedule of functional goal achievement
á
Operational competency achievement dates
á
Functional communication goals achievement dates
á
Treatment plan with a training schedule for the selected
device and accessories
á
Type of Treatment (individual vs. group)
á
Projected Frequency of Reassessment
á
Follow-up Requirements for SGD and Accessories
o
Individual(s) responsible for programming
o
Individual(s) responsible for troubleshooting
Section 7:
Functional Benefit of Upgrade
á If the
recommendation is for an upgrade of a device, provide documentation as to what
has changed with the individualsÕ medical status and/or why their current SGD
does not meet their medical needs.
Section 8: SLP Assurance of
Financial Independence and Signature
á The report
should state: "The SLP performing this evaluation is not an employee
of and does not have a financial relationship with the supplier of any
SGD."
á SLP signature
á Evaluating SLP's
name & contact information (agency, address & telephone number)
á ASHA Certification
Number
á
State License Number
================================================================================================================
EXAMPLE 5 BY LINGRAPHICA

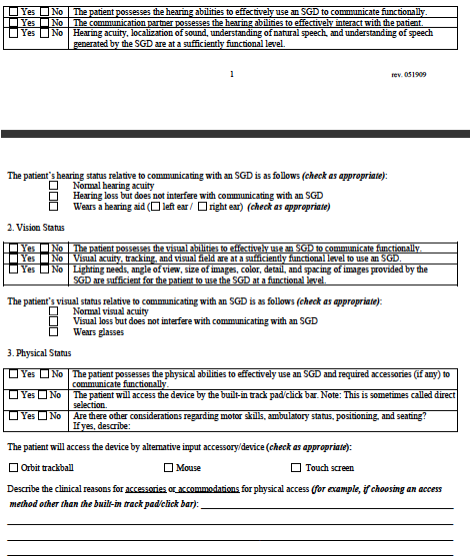

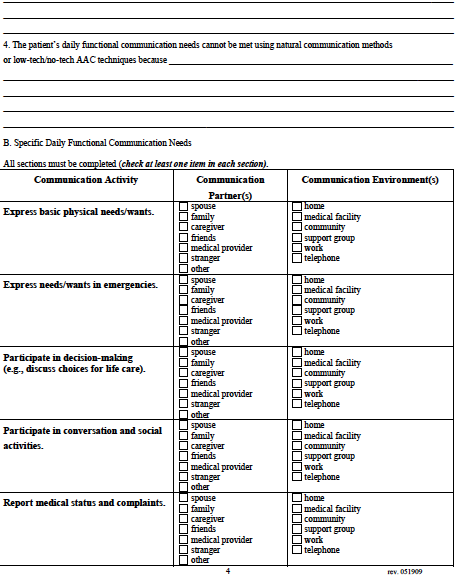
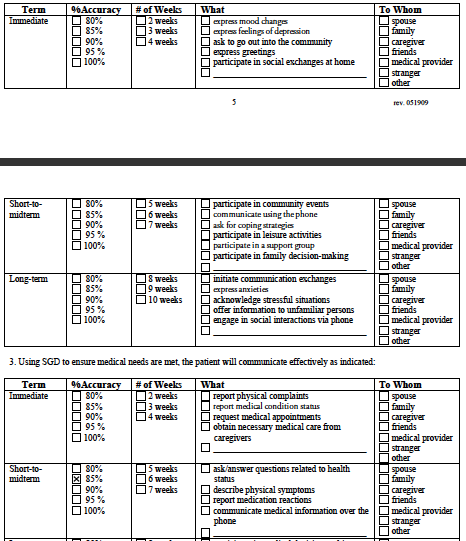

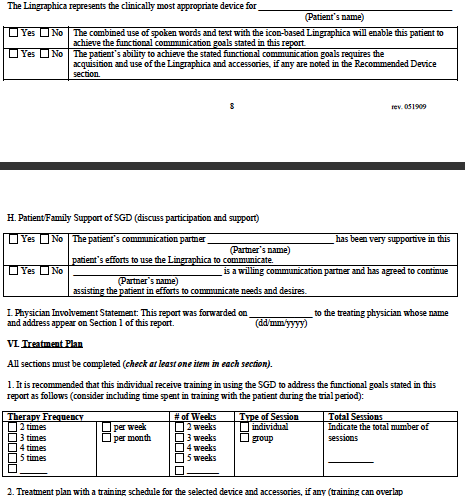


========================================================================================================
EXAMPLE 6 BY TOBII: