The Chicken AND The Egg
SED 695B
Biology/Life Sciences - Grades Nine Through Twelve
Evolution
7. The frequency of an allele in a gene pool of a population depends on many factors and may be stable or unstable over time. As a basis for understanding this concept:
c.Students know variation within a species increases the likelihood that at least some members of a species will survive under changed environmental conditions.
8. Evolution is the result of genetic changes that occur in constantly changing environments. As a basis for understanding this concept:
f. Students know how to use comparative embryology, DNA or protein sequence comparisons, and other independent sources of data to create a branching diagram (cladogram) that shows probable evolutionary relationships.
After researching comparative embryonic development, students examine the contents of a fertilized chicken egg. Once the shell is broken, the student identify the yolk and the embryonic cells. The will then examine these cells under a microscope.
Supplies:
-Non-viable fertilized eggs were used in this experiment. Such eggs can be obtained from an organic foods store or a wholesale egg distributor.
-Many types of microscopes will serve the purpose of this lab. They key is to find a well-lit, low power device. In the included images, pcitures taken from an electronic micrsope (Pro-scope) at a maginification of 25x are shown along with dissecting microscope images of 2x and 4x.
Other related experiments have been conducted using developing eggs and/or more sophisticated microscopy tools. The results tend to be cleaer and more successful with these methods, but the specimens and instruments are more difficult to come by.
Lab Set Up:
 |
 |
 |
Super Market Fertilized Eggs ($3.50) |
Egg Farm Fertilized Eggs ($10.00) |
Dissecting Microscope (Priceless?) |
Questions:
Which image shows anterior, and which image shows posterior, 1 or 2?
Can you find the heart in image 3?
How many structures can you identify in image 4?
Can you find the outline of the embryo in image 5?
What is the sturcture pointed to in image 6?
Image #1

Image #2

Image #3

Image #4
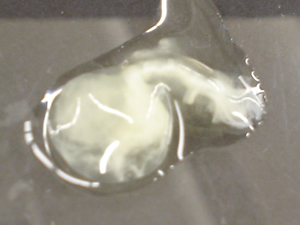
Image #5
Image #6
Solution to Question Above:
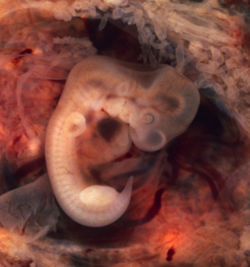
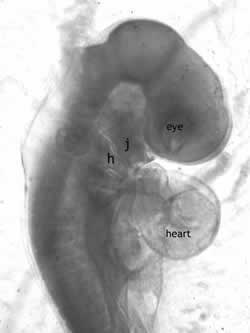
Image A is a human embryo and Image B is that of a chicken.
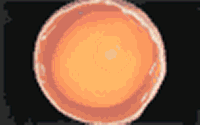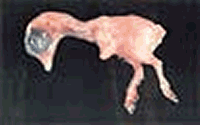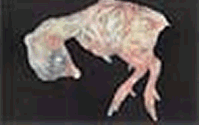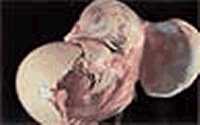
The embryo preparation, photos and text are by Dr. Gayner McDaniel, Poultry Science Department, Auburn University, Auburn, Alabama. These images appear on a poster that is provided to classrooms in Lancaster County, Nebraska using the 4-H School Enrichment Embryology project.
| References & Links: | 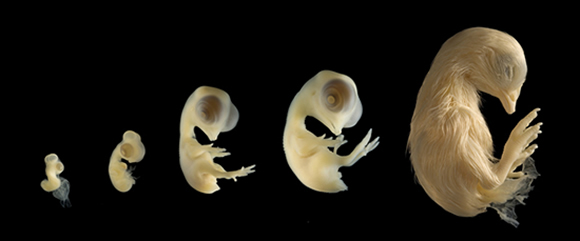 |
| 4-H Embryology | |
| Black Line Diagrams and Quizes | |