
INDUCTIVE REASONING
Mitosis | Pendulum | Seismic Activity
INDUCTIVE REASONING:
"Induction is a major kind of reasoning process in which a conclusion is drawn from particular cases. It is usually contrasted with deduction, the reasoning process in which the conclusion logically follows from the premises, and in which the conclusion has to be true if the premises are true. In inductive reasoning, on the contrary, there is no logical movement from premises to conclusion. The premises constitute good reasons for accepting the conclusion. The premises in inductive reasoning are usually based on facts or observations. There is always a possibility, though, that the premises may be true while the conclusion is false, since there is not necessarily a logical relationship between premises and conclusion." From: Grolier's 1994 Multimedia Encyclopedia
Inductive reasoning is used when generating hypotheses, formulating theories and discovering relationships, and is essential for scientific discovery.
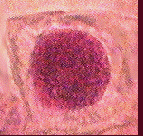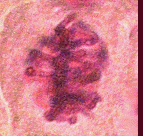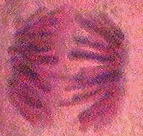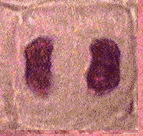
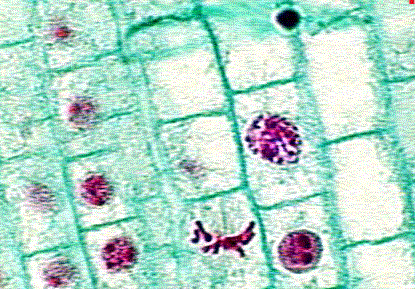
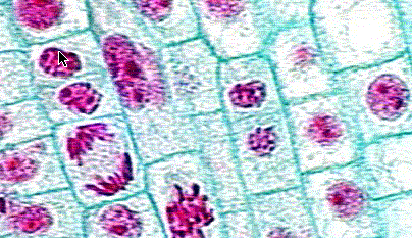
EXAMPLE 1: MITOSIS. What hypotheses can you generate from the following data?
Number of cells found in each phase
| Sample | Interphase | Prophase | Metaphase | Anaphase | Telophase |
| 1 | 45 | 15 | 5 | 3 | 5 |
| 2 | 89 | 23 | 5 | 4 | 9 |
| 3 | 101 | 17 | 6 | 2 | 8 |
| 4 | 67 | 27 | 3 | 1 | 7 |
| 5 | 88 | 34 | 6 | 0 | 8 |
| 6 | 77 | 33 | 3 | 2 | 5 |
| 7 | 89 | 24 | 5 | 3 | 7 |
| 8 | 45 | 12 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 9 | 68 | 12 | 4 | 5 | 6 |

Pendulums
On the basis of the following data, derive a formula that describes the relationship between mass, length and period of a pendulum. (see syllabus)
Sesismic Activity
(1) Plot this week's earthquakes on a map of the world.
(2) Identify all volcanoes
(3) What inferences can you make from this map?