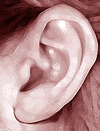
| Attached earlobes
|
 |
Unattached earlobes | 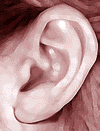 |
| tongue-roller |  |
Non -tongue roller |  |
| hitch-hiker's thumb |  |
straight thumb |  |
Genetics Phenotype Survey
Download Genetics Spreadsheet File | Mitosis
Identify chromosomes (karyotyping)
| Characteristic: d=dominant / r=recessive | Personal Phenotype and Genotype | Number w/trait | % of Class with Trait |
|---|---|---|---|
Hairline
|
|||
Earlobes
|
|||
Hair on middle segment of finger (dorsal side)
|
|||
Interlocking fingers
|
|||
Hitchhiker's thumb
|
|||
Bent little finger
|
|||
U-shaped tongue
|
|||
PTC taster
|
|||
Thiourea taster
|
|||
Sodium benzoate taster
|
|||
Colorblindness
|
| Attached earlobes
|
 |
Unattached earlobes |  |
| tongue-roller |  |
Non -tongue roller |  |
| hitch-hiker's thumb |  |
straight thumb |  |
 |
 |
|
| VISUAL ACUITY: A person who has sufficient visual acuity should see the number twelve in the circle on the left whether or not they have normal color vision. I | COLOR BLINDNESS: A person with normal color vision sees a number seven in the circle on the left. Those who are color blind usually do not see any number at all. | |
 |
 |
|
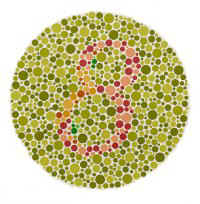
| RED-GREEN COLORBLINDNESS: People with red-green color blindness see either a three or nothing at all. Those with normal color vision see an 8. | PROTANOPIA & DEUTERANOPIA Those with normal vision see the number thirty-five in the circle above. A person with protanopia sees tonly he number five. A person with deuteranopia sees the number three. People who are partially color blind will see both numbers but one more distinctly than the other. |