
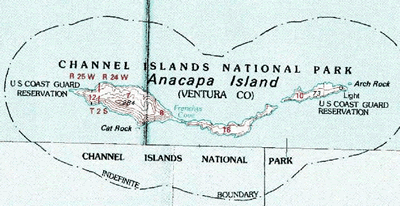

Anacapa Island |
||
| Author(s): Jim Mauch | Field Trip -
Teacher's Guide SED 695B; Fall 2005 |
|
   |
||
Topics addressed
|
Description of Field Trip This field trip will begin at Ventura Harbor, where we will board the Islander, one of Island Packer's trimarans. It will take about an hour to get to the island, unless we are lucky enough to come across migrating whales. This is a full day field trip to explore the biology and geology of a relatively undisturbed area of the California coast. During the trip, students will:
The activities we will actually complete will depend upon many factors, including weather, and how much time we spend with whales. Things to bring:
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Standards Ecology
Dynamic Earth Processes
California Geology
|
Study Guide: A log booklet will be provided for you to write all of your notes and observations. this is a compressed copy of its contents. Anacapa Field ObservationGeneral observations:
|
Questions:
|
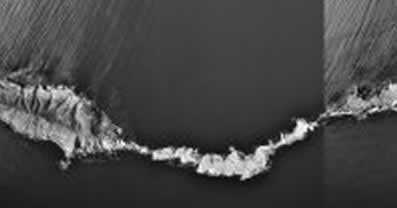 |
This photograph shows that anacapa is actually three islands. The two sections to the west are closed to visitors as they are important habitat to sea birds. We will actually be hiking on the eastern segment (on the right of the photo. |
 |
The islander has several display screens for you to use to collect navigation data. Be sure to select a time with your instructor, so that your data can be used to plot our course. |
 |
As we cruise down the coast of Anacapa, be sure to observe the behaviors of the Brown Pelicans and the gulls. You are likely to see quite a show. |
 |
When we arrive, we will disembark from the bow to a small landing. Be sure you have all of your things with you. The boat does not stay here. |
 |
Before our lunch and hike, we will get a little exercise climbing the many steps up to the plateau on the top of the island. |
 |
A short walk to the visitor center, where we will eat lunch and meet our guide. |
 |
The interpreter o our hike will either be a volunteer from the National Park Service, or one of Island Packers' staff. We will go on a short walk around the island with many stops. Be sure to look for important information to add to your field log. |
| Description / questions | |
 |
Can you identify the species of gulls you see? Ask your instructor for field guides and look closely for distinguishing marks and colors on the feet and beak. |
 |
Take the time to watch the behaviors of the animals you see. |
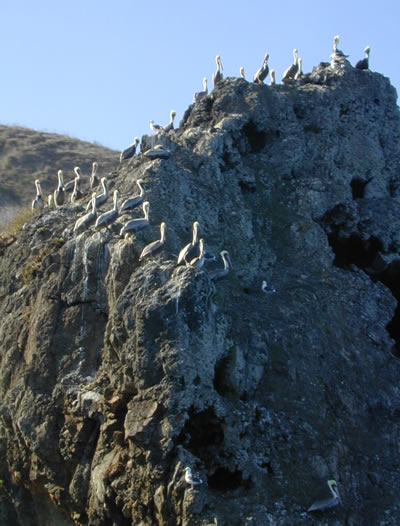 |
Why is the presence of so many Brown Pelicans on Anacapa considered a remarkable thing? What has put them on the brink of extinction and continues to threaten them today? |
 |
All of the little white specks on this picture are birds. They play an important role in the ecology of the islands. Describe their role in the ecology of the marine environment surrounding the island. |
 |
What events triggered the construction of a lighthouse on the island? What other evidence of human activity on the island do you see? What is the estimated population size of Chumash on the Channel Islands prior to contact with Europeans? |
 |
Listen closely as your guide describes native plants on the island. |
 |
The taller, brown plants in the background of this picture are giant coreopsis. They will most likely look much different when you see them. |
 |
What is this plant? Is this native to the island? What are the reasons for its presence here? What programs are under way involving this plant? |
 |
After our tour of the island, we will be met on the dock by some of the crew who will have some samples of the marine invertebrates inhabiting these waters. Have your log book ready. You will learn a great deal about their niche in this ecosystem. Later, after we board, we will collect a plankton sample. You will have the opportunity to observe and identify species fron that sample. |
 |
On the way home, keep your eyes open. there is till plenty of time to see something new. |
References & Links: Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary
|
|