Rain Water Survey Kit? - pH
SED 695B; Fall 2005
Overview: pH is a measure of the negative log of the hydrogen ions in a solution.
The pH of a solution can be found by using chemically treated paper which turns different colours in the presence of hydrogen ions. By comparing the colour of the pH paper to the colour code on the package, one can assertain the pH of a solution.

Topics addressed:
pH
acid and bases
water quality testing
Experiment
The origin of the pH scale came out of necessity since hydrogen ion concentrations in a typical experiment could range from 0.01 M to 0.0000000000001 M. The logrthymic scale changes this to a managable pH 2 to 13. The origin of the word pH came from the German word potenz which means power, so pH is the power of hydrogen.
Many molecules respond differently in acids than in bases, however it is those chemicals that have a discernable change that are useful. Onions, for example, can be used to detect bases since they don't smell in bases.
For our purposes colour change is more appropriate. The basic formula for an indicator solution is:
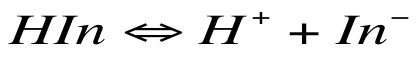
HIn refers to the molecule with the hydrogen ion attached, and In is the indicator without the hydrogen atom. H is the hydrogen atom.
We would desire a molecule that has different colours both as an indicator alone and when the hydrogen ion attach to it. See references for a list of indicators.
Standards addressed:
8th grade Physical Science
5a. Students know how to determine whether a solution is acidic, basic, or neutral.
Chemistry (9th-12th)
5d. Students know how to use the pH scale to characterize acid and base solutions.
Procedure:
1. Pull out a 5cm piece of pH paper from the roll. Be sure to use tweezers. Do not touch the paper with your hands. The oils from your hands could effect the results.
2. Dip the pH paper into the solution. You must have the material you wish to test in solution. If it is a solid, like soil, test the pH of some distilled water first. Then add the distilled water to the soil. Retest the soil with the water.
3. While the paper is still moist, compare the colour to the colour chart provided in the pH paper roll.
4. Record the pH into you data sheet and dispose of the pH paper. It should not be reused.
Questions:
1. Why is pH an important measure?
2. Where does acid rain come from?
3. If the pH of water is 7.0, is the water safe to drink?



References & Links:
Why do molecules change color in response to pH changes?