Instrumentation: The (very cool) Floating Tin Sponge
Author(s): Denise Agapoff
& the Fabulous Tom Schuster
SED 695B; Fall 2005
Overview:
When mossy zinc is added to an acidic stannous chloride solution, two
single replacement reactions occur. The products are tin metal, zinc
chloride and hydrogen gas.
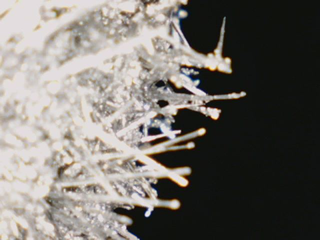
(To the left is the tin produced from this reaction)

Topics addressed:
-
Chemical change
-
Density
-
Single replacement reaction
-
Reaction of acid & metal
Chemical Reactions:
Zn(s) + SnCl2(aq) ---› ZnCl2(aq) + Sn(s)
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) ---› ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
California State High School Standards:
5a. Students know the observable properties of acid
solutions.
7b. Students know chemical processes can either release
(exothermic) or absorb (endothermic) thermal energy.
California State 8th Physical Science Standards:
5aStudents know reactant atoms and molecules interact
to form products with different chemical properties.
8a. Students know density is mass per unit volume.
8b.Students know how to calculate the density of substances
(regular and irregular solids and liquids) from measurements of mass
and volume.
Procedure:
- Add 200 mL of acidic stannous chloride to a 500 mL beaker. The amount of the solution does not have to be exact. Use the graduations on the beaker for your measurements.
- Observe the physical properties of the zinc.
- Add about 12 pieces of mossy zinc to the beaker. Observe reaction.
- After a couple of minutes, the newly formed tin can be removed with tongs. DO NOT handle tin at this point.
- The tin should be rinsed thoroughly under running water and dried on paper towels.
- If the tin is left in the solution several more minutes, it will float to the surface.
- Observe the physical properties of the tin.
Clean-up:
- The elemental tin should be rinsed thoroughly under running water, dried and disposed of in the trash.
- The acidic stannous chloride solution should be neutralized by adding sodium bicarbonate to it. After neutralization, the solution may be flushed down the drain with excess water.
Possible questions for students:
- What clue(s) are there that this reaction is chemical and/or physical?
- Is this reaction endothermic or exothermic?
- How could you test to see if the gas given off is really hydrogen gas?
- What is the density of each metal?

Materials:
-
Acidic stannous chloride solution
- Mossy zinc
- 500 mL beaker
- Tongs
- Paper towel
- Chemical resistant gloves
- Safety goggles

Procedure:
To involve students, allow each pair of students to add one of the pieces of zinc to the beaker.
The Chemical Reaction:
From behind your safety goggles, look for clues that a chemical reaction is taking place.
If left in the solution long enough, the tin will float to the surface.

Clean-up:
The acidic stannous chloride solution is toxic and corrosive to skin and eyes. Thoroughly rinse the elemental tin

mossy zinc and newly formed tin
Comparing Metals:
The mossy zinc on the left has very different physical properties compared to the newly formed elemental tin.
|
|
These crystals are the newly formed tin |
 |
 |
 |
|
References & Links:
- Where to buy this kit: http://www.flinnsci.com/
- Online tutorial for chemical reactions: http://www.chemtutor.com/react.htm#single
- Worksheet for chemical reactions: http://misterguch.brinkster.net/CONT12.pdf#search='single%20replacement%20reaction'
- Online chemical and physical tutorials: http://www.fordhamprep.com/gcurran/sho/sho/lessons/lesson15.htm